One-stage freehand minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with mini-access surgery through OLIF approach for the treatment of lumbar tuberculosis
- PMID: 35440015
- PMCID: PMC9019983
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-022-03130-4
One-stage freehand minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation combined with mini-access surgery through OLIF approach for the treatment of lumbar tuberculosis
Abstract
Objective: To compare one-stage freehand minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation (freehand MIPS) combined with mini-access surgery through OLIF approach with posterior approach for treatment of lumbar tuberculosis (TB), and evaluate its feasibility, efficacy and safety in debridement, bone graft fusion and internal fixation.
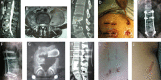
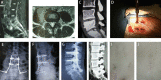
Methods: 48 patients with single segment lumbar TB from June 2014 to June 2017 were included. Among them, 22 patients underwent one-stage freehand MIPS combined with mini-access surgery through OLIF approach (group 1), 26 patients were treated with posterior open surgery (group 2). Duration of operation, blood loss, and stay time in hospital were compared. Pre- and postoperative visual analog scale (VAS) pain scores, Oswestry disability index (ODI), erythrocyte sedimentation rate, complications and images were also recorded.
Results: Patients in group 1 showed significantly less blood loss (165 ± 73 ml vs 873 ± 318 ml, P < 0.001), shorter stay time in hospital (6/4-8 days vs 12/8-15 days, P < 0.001), while longer duration of operation (185 ± 14 min vs 171 ± 12 min, P < 0.001) than group 2 did. VAS scores significantly decreased after surgery in both groups, however, VAS scores of group 1 were significantly lower than that of group 2 immediately after surgery and during follow-ups (P < 0.001). ODI of group 1 was also significantly lower than that of group 2 at 12-month after surgery (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: One-stage freehand MIPS combined with mini-access surgery through OLIF approach is a feasible, efficient and safe method in treating single segment lumbar TB. It shows advantages of less surgical trauma and faster postoperative recovery.
Keywords: Bone graft fusion; Debridement; Lumbar tuberculosis; Minimally invasive spine surgery; OLIF; Pedicle screw fixation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Du X, Ou YS, Zhu Y, Luo W, Jiang GY, Jiang DM. Oblique lateral interbody fusion combined percutaneous pedicle screw fixation in the surgical treatment of single-segment lumbar tuberculosis: a single-center retrospective comparative study. Int J Surg. 2020;83:39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.09.012. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

