Evaluation of fully automated cephalometric measurements obtained from web-based artificial intelligence driven platform
- PMID: 35440037
- PMCID: PMC9020017
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02170-w
Evaluation of fully automated cephalometric measurements obtained from web-based artificial intelligence driven platform
Abstract
Background: Artificial Intelligence has created a huge impact in different areas of dentistry. Automated cephalometric analysis is one of the major applications of artificial intelligence in the field of orthodontics. Various automated cephalometric software have been developed which utilizes artificial intelligence and claim to be reliable. The purpose of this study was to compare the linear and angular cephalometric measurements obtained from web-based fully automated Artificial Intelligence (AI) driven platform "WebCeph"™ with that from manual tracing and evaluate the validity and reliability of automated cephalometric measurements obtained from "WebCeph"™.
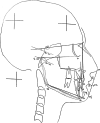
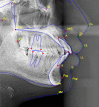
Methods: Thirty pre-treatment lateral cephalograms of patients were randomly selected. For manual tracing, digital images of same cephalograms were printed using compatible X-ray printer. After calibration, a total of 18 landmarks was plotted and 12 measurements (8 angular and 4 linear) were obtained using standard protocols. The digital images of each cephalogram were uploaded to "WebCeph"™ server. After image calibration, the automated cephalometric measurements obtained through AI digitization were downloaded for each image. Intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was used to determine agreement between the measurements obtained from two methods. ICC value < 0.75 was considered as poor to moderate agreement while an ICC value between 0.75 and 0.90 was considered as good agreement. Agreement was rated as excellent when ICC value > 0.90 was obtained.
Results: All the measurements had ICC value above 0.75. A higher ICC value > 0.9 was obtained for seven parameters i.e. ANB, FMA, IMPA/L1 to MP (°), LL to E-line, L1 to NB (mm), L1 to NB (°), S-N to Go-Gn whereas five parameters i.e. UL to E-line, U1 to NA (mm), SNA, SNB, U1 to NA (°) showed ICC value between 0.75 and 0.90.
Conclusion: A good agreement was found between the cephalometric measurements obtained from "WebCeph"™ and manual tracing.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Lateral cephalogram; WebCeph™.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Steiner CC. The use of cephalometrics as an aid to planning and assessing orthodontic treatment. Am J Orthod. 1960;46:721–735. doi: 10.1016/0002-9416(60)90145-7. - DOI
-
- Ricketts RM. Perspectives in the clinical application of cephalometrics: the first fifty years. Angle Orthod. 1981;51:115–150. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

