Prognostic value and biological function of LRRN4 in colorectal cancer
- PMID: 35440048
- PMCID: PMC9020117
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-022-02579-x
Prognostic value and biological function of LRRN4 in colorectal cancer
Abstract
Background: Several nervous and nerve-related biomarkers have been detected in colorectal cancer (CRC) and can contribute to the progression of CRC. However, the role of leucine-rich repeat neuronal 4 (LRRN4), a recently identified neurogenic marker, in CRC remains unclear.
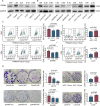
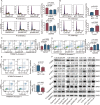
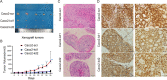
Methods: We examined the expression and clinical outcomes of LRRN4 in CRC from TCGA-COREAD mRNA-sequencing datasets and immunohistochemistry in a Chinese cohort. Furthermore, colony formation, flow cytometry, wound healing assays and mouse xenograft models were used to investigate the biological significance of LRRN4 in CRC cell lines with LRRN4 knockdown or overexpression in vitro and in vivo. In addition, weighted coexpression network analysis, DAVID and western blot analysis were used to explore the potential molecular mechanism.
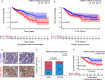
Results: We provide the first evidence that LRRN4 expression, at both the mRNA and protein levels, was remarkably high in CRC compared to controls and positively correlated with the clinical outcome of CRC patients. Specifically, LRRN4 was an independent prognostic factor for progression-free survival and overall survival in CRC patients. Further functional experiments showed that LRRN4 promoted cell proliferation, cell DNA synthesis and cell migration and inhibited apoptosis. Knockdown of LRRN4 can correspondingly decrease these effects in vitro and can significantly suppress the growth of xenografts. Several biological functions and signaling pathways were regulated by LRRN4, including proteoglycans in cancer, glutamatergic synapse, Ras, MAPK and PI3K. LRRN4 knockdown resulted in downregulation of Akt, p-Akt, ERK1/2 and p-ERK1/2, the downstream of the Ras/MAPK signaling pathway, overexpression of LRRN4 leaded to the upregulation of these proteins.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that LRRN4 could be a biological and molecular determinant to stratify CRC patients into distinct risk categories, and mechanistically, this is likely attributable to LRRN4 regulating several malignant phenotypes of neoplastic cells via RAS/MAPK signal pathways.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Leucine-rich repeat neuronal 4; Neurogenic biomarker; Prognosis; RAS/MAPK signal pathways.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Role of LRRN4 in promoting malignant behavior in a p53- and Rb-defective human fallopian tube epithelial cell line.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3324-3341. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37693155 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of SNTB1 correlates with poor prognosis and promotes cell growth by negative regulating PKN2 in colorectal cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2021 Oct 18;21(1):547. doi: 10.1186/s12935-021-02246-7. Cancer Cell Int. 2021. PMID: 34663329 Free PMC article.
-
KIFC3 Promotes Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in Colorectal Cancer via PI3K/AKT/mTOR Signaling Pathway.Front Genet. 2022 Jun 22;13:848926. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.848926. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35812733 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of CIP2A and its mechanism of action in the malignant biological behavior of colorectal cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Apr 22;18(1):67. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00545-6. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32321509 Free PMC article.
-
Granulin epithelin precursor promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by activating MARK/ERK pathway.J Transl Med. 2018 Jun 4;16(1):150. doi: 10.1186/s12967-018-1530-7. J Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29866109 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Leukotriene B4 receptor knockdown affects PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling and apoptotic responses in colorectal cancer.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Jan 20;24(4):968-981. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10119. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38259082 Free PMC article.
-
Network pharmacology and molecular docking to elucidate the mechanism of pulsatilla decoction in the treatment of colon cancer.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 8;13:940508. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.940508. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36003525 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment of a novel mouse model of colorectal cancer by orthotopic transplantation.BMC Cancer. 2025 Mar 6;25(1):405. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13834-5. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40050746 Free PMC article.
-
Role of LRRN4 in promoting malignant behavior in a p53- and Rb-defective human fallopian tube epithelial cell line.Am J Cancer Res. 2023 Aug 15;13(8):3324-3341. eCollection 2023. Am J Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37693155 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

