Trilobite-inspired neural nanophotonic light-field camera with extreme depth-of-field
- PMID: 35440101
- PMCID: PMC9019092
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29568-y
Trilobite-inspired neural nanophotonic light-field camera with extreme depth-of-field
Abstract
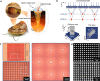
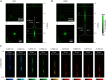
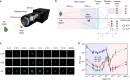
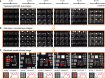
A unique bifocal compound eye visual system found in the now extinct trilobite, Dalmanitina socialis, may enable them to be sensitive to the light-field information and simultaneously perceive both close and distant objects in the environment. Here, inspired by the optical structure of their eyes, we demonstrate a nanophotonic light-field camera incorporating a spin-multiplexed bifocal metalens array capable of capturing high-resolution light-field images over a record depth-of-field ranging from centimeter to kilometer scale, simultaneously enabling macro and telephoto modes in a snapshot imaging. By leveraging a multi-scale convolutional neural network-based reconstruction algorithm, optical aberrations induced by the metalens are eliminated, thereby significantly relaxing the design and performance limitations on metasurface optics. The elegant integration of nanophotonic technology with computational photography achieved here is expected to aid development of future high-performance imaging systems.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Clarkson ENK. Schizochroal eyes and vision in some Silurian acastid trilobites. Palaeontology. 1966;9:1–29.
-
- Ihrke I, Restrepo J, Mignard-Debise L. Principles of light field imaging. IEEE Signal. Proc. Mag. 2016;33:59–69. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2582220. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

