The correlation of lncRNA SNHG16 with inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, disease severity, and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke patients
- PMID: 35441431
- PMCID: PMC9169180
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24439
The correlation of lncRNA SNHG16 with inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, disease severity, and prognosis in acute ischemic stroke patients
Abstract
Background: Long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 16 (lncRNA SNHG16) is involved in the pathogenesis of acute ischemic stroke (AIS) through the regulation of brain endothelial cell viability, inflammation, atherosclerotic plaque formation, and neural apoptosis. This study aimed to evaluate the prognostic value of lncRNA SNHG16 in AIS patients.
Methods: Newly diagnosed AIS patients (N = 120) were serially recruited. Their lncRNA SNHG16 expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were detected by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR); serum inflammatory cytokines and adhesion molecules were determined using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The accumulating recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) were analyzed. Moreover, controls (N = 60) were recruited and their lncRNA SNHG16 expressions in PBMCs were detected.
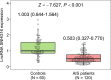
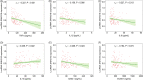
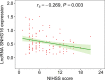
Results: LncRNA SNHG16 was declined in AIS patients compared to controls (p < 0.001). Moreover, lncRNA SNHG16 was not related to any comorbidities in AIS patients (all p > 0.05). Interestingly, lncRNA SNHG16 was negatively related to tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) (p < 0.001), interleukin 6 (IL-6) (p = 0.013), and intracellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) (p = 0.024), while positively correlated with interleukin 10 (IL-10) (p = 0.022) in AIS patients. Besides, lncRNA SNHG16 was inversely associated with the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score in AIS patients (p = 0.003). During the follow-up period, in 14 (11.7%) patients occurred recurrence and 5 (4.2%) patients died. Unexpectedly, lncRNA SNHG16 was not associated with accumulating RFS (p = 0.103) or OS (p = 0.150) in AIS patients.
Conclusion: LncRNA SNHG16 relates to lower inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, and milder disease severity, but fails to predict prognosis in AIS patients.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; disease severity; inflammatory cytokines; long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 16; prognosis.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Mendelson SJ, Prabhakaran S. Diagnosis and management of transient ischemic attack and acute ischemic stroke: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(11):1088‐1098. - PubMed
-
- Rabinstein AA. Update on treatment of acute ischemic stroke. Continuum (Minneap Minn). 2020;26(2):268‐286. - PubMed
-
- Zhu F, Gauberti M, Marnat G, et al. Time from I.V. Thrombolysis to thrombectomy and outcome in acute ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol. 2021;89(3):511‐519. - PubMed
-
- Singh RJ, Chen S, Ganesh A, Hill MD. Long‐term neurological, vascular, and mortality outcomes after stroke. Int J Stroke. 2018;13(8):787‐796. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

