Impaction Bone Grafting Combined with Titanium Mesh for Acetabular Bone Defects Reconstruction in Total Hip Arthroplasty Revision: A Retrospective and Mini-Review Study
- PMID: 35441498
- PMCID: PMC9087461
- DOI: 10.1111/os.13262
Impaction Bone Grafting Combined with Titanium Mesh for Acetabular Bone Defects Reconstruction in Total Hip Arthroplasty Revision: A Retrospective and Mini-Review Study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the application of impaction bone grafting (IBG) combined with Ti-alloy mesh for acetabular bone defect reconstruction in total hip arthroplasty (THA) revision and follow up the clinical outcomes and imaging findings.
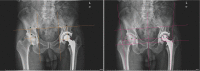
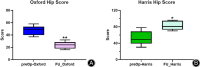
Methods: The clinical and imaging data of patients who were admitted to our hospital from January 2000 to December 2020 and underwent acetabular bone defects reconstruction using IBG combined with titanium mesh were retrospectively analyzed. Preoperative and post-revision Oxford and Harris scores, and post-revision complications were evaluated. Radiographs were used to determine center of rotation (COR) of the hip joint, transparency line, bone graft fusion, and bone mineral density (BMD) around the hip joint.
Results: Significant improvement was observed in both Oxford and Harris scores (P < 0.05). The radiographs taken at the last follow-up examination showed no significant differences in the acetabulum COR, offsets, inclination angle, mean ratio of vertical value, and BMD analysis between the post-revision side and contralateral side (P > 0.05). The follow-up data showed restoration of the mesh implant and graft bone fusion.
Conclusions: The application of IBG combined with titanium-alloy mesh in revision THA patients with acetabular defects was found to provide satisfactory outcomes. However, large-scale studies are still needed to further elucidate the long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Acetabular defects; Bone mineral density; Impaction bone grafting; Revision; Total hip arthroplasty.
© 2022 The Authors. Orthopaedic Surgery published by Tianjin Hospital and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Learmonth ID, Young C, Rorabeck C. The operation of the century: total hip replacement. Lancet. 2007;370:1508–19. - PubMed
-
- Sukhonthamarn K, Grosso MJ, Sherman MB, Restrepo C, Parvizi J. Risk factors for unplanned admission to the intensive care unit after elective total joint arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2020;35:1937–40. - PubMed
-
- Sloan M, Premkumar A, Sheth NP. Projected volume of primary total joint arthroplasty in the U.S., 2014 to 2030. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2018;100:1455–60. - PubMed
-
- Bian Y, Cheng K, Chang X, Weng X. Reports and analysis of amount of hip and knee arthroplasty in China from 2011 to 2019. Chin J Orthop. 2020;40:1453–60.
-
- Gross AE, Goodman S. The current role of structural grafts and cages in revision arthroplasty of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;429:193–200. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

