Comorbidities of sarcoidosis
- PMID: 35441568
- PMCID: PMC9891229
- DOI: 10.1080/07853890.2022.2063375
Comorbidities of sarcoidosis
Abstract
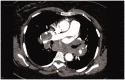
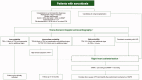
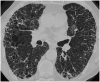
Sarcoidosis is a heterogeneous disease, which can affect virtually every body organ, even though lungs and intra thoracic lymph nodes are almost universally affected. The presence of noncaseating granulomas is the histopathological hallmark of the disease, and clinical picture depends on the organs affected. Data about interaction between sarcoidosis and comorbidities, such as cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases, autoimmune disorders, malignancy and drug-related adverse events are limited. Several lung conditions can be associated with sarcoidosis, such as pulmonary hypertension and fibrosis, making it difficult sometimes the differentiation between complications and distinctive pathologies. Their coexistence may complicate the diagnosis of sarcoidosis and contribute to the highly variable and unpredictable natural history, particularly if several diseases are recognised. A thorough assessment of specific disorders that can be associated with sarcoidosis should always be carried out, and future studies will need to evaluate sarcoidosis not only as a single disorder, but also in the light of possible concomitant conditions.Key messagesComorbidities in sarcoidosis are common, especially cardiovascular and pulmonary diseases.In the diagnostic workup, a distinction must be made between sarcoidosis-related complaints and complaints caused by other separate disorders. It can be very difficult to distinguish between complications of sarcoidosis and other concomitant conditions.The coexistence of multiple conditions may complicate the diagnosis of sarcoidosis, affect its natural course and response to treatment.
Keywords: Adverse drug reactions; comorbidity; heart disease; multidisciplinary management; pulmonary hypertension; sarcoid-like reaction; sarcoidosis; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Claudio Tana is the Section Editor of the Primary Care section of Annals of Medicine.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
