A new prediction model for ventricular arrhythmias in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 35441664
- PMCID: PMC9392651
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac180
A new prediction model for ventricular arrhythmias in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to: A new prediction model for ventricular arrhythmias in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy.Eur Heart J. 2022 Jul 21;43(28):2712. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehac181. Eur Heart J. 2022. PMID: 35441672 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
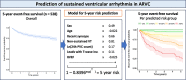
Aims: Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is characterized by ventricular arrhythmias (VAs) and sudden cardiac death (SCD). We aimed to develop a model for individualized prediction of incident VA/SCD in ARVC patients.
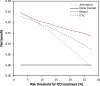
Methods and results: Five hundred and twenty-eight patients with a definite diagnosis and no history of sustained VAs/SCD at baseline, aged 38.2 ± 15.5 years, 44.7% male, were enrolled from five registries in North America and Europe. Over 4.83 (interquartile range 2.44-9.33) years of follow-up, 146 (27.7%) experienced sustained VA, defined as SCD, aborted SCD, sustained ventricular tachycardia, or appropriate implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) therapy. A prediction model estimating annual VA risk was developed using Cox regression with internal validation. Eight potential predictors were pre-specified: age, sex, cardiac syncope in the prior 6 months, non-sustained ventricular tachycardia, number of premature ventricular complexes in 24 h, number of leads with T-wave inversion, and right and left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEFs). All except LVEF were retained in the final model. The model accurately distinguished patients with and without events, with an optimism-corrected C-index of 0.77 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.73-0.81] and minimal over-optimism [calibration slope of 0.93 (95% CI 0.92-0.95)]. By decision curve analysis, the clinical benefit of the model was superior to a current consensus-based ICD placement algorithm with a 20.3% reduction of ICD placements with the same proportion of protected patients (P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Using the largest cohort of patients with ARVC and no prior VA, a prediction model using readily available clinical parameters was devised to estimate VA risk and guide decisions regarding primary prevention ICDs (www.arvcrisk.com).
Keywords: Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy; Implantable cardioverter-defibrillators; Sudden cardiac death; Ventricular arrhythmias.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: H.C. is a consultant for Medtronic Inc. and St. Jude Medical/Abbott. H.C. receives research support from Boston Scientific Corp. C.T. and C.A.J. receive salary support from this grant. C.A.J. has received funding for an invited lecture from Abbott. H.T. receives research support from Abbott. A.A.M.W. received a personal fee from Audentes 2017. A.M.S. received lecture honoraria from Boston Scientific Corp. S.L.Z. receives salary support as an advisor to Siemens Healthcare. D.P.J. is a consultant for Pfizer, GSK, and Blade Therapeutics, and receives research support from NIH, Eidos Therapeutics, and Array Biopharma. The rest of the authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Corrado D, Wichter T, Link MS, Hauer R, Marchlinski F, Anastasakis A, Bauce B, Basso C, Brunckhorst C, Tsatsopoulou A, Tandri H, Paul M, Schmied C, Pelliccia A, Duru F, Protonotarios N, Estes NA 3rd, McKenna WJ, Thiene G, Marcus FI, Calkins H.. Treatment of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia: an international task force consensus statement. Eur Heart J 2015;36:3227–3237. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhonsale A, James CA, Tichnell C, Murray B, Gagarin D, Philips B, Dalal D, Tedford R, Russell SD, Abraham T, Tandri H, Judge DP, Calkins H.. Incidence and predictors of implantable cardioverter-defibrillator therapy in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy undergoing implantable cardioverter-defibrillator implantation for primary prevention. J Am Coll Cardiol 2011;58:1485–1496. - PubMed
-
- Corrado D, Calkins H, Link MS, Leoni L, Favale S, Bevilacqua M, Basso C, Ward D, Boriani G, Ricci R, Piccini JP, Dalal D, Santini M, Buja G, Iliceto S, Estes NA 3rd, Wichter T, McKenna WJ, Thiene G, Marcus FI.. Prophylactic implantable defibrillator in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy/dysplasia and no prior ventricular fibrillation or sustained ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 2010;122:1144–1152. - PubMed
-
- Schuler PK, Haegeli LM, Saguner AM, Wolber T, Tanner FC, Jenni R, Corti N, Luscher TF, Brunckhorst C, Duru F.. Predictors of appropriate ICD therapy in patients with arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: long term experience of a tertiary care center. PLoS One 2012;7:e39584.. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bosman LP, Sammani A, James CA, Cadrin-Tourigny J, Calkins H, van Tintelen JP, Hauer RNW, Asselbergs FW, Te Riele A. Predicting arrhythmic risk in arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm 2018;15:1097–1107. - PubMed

