Immunomodulatory and direct activities of ropeginterferon alfa-2b on cancer cells in mouse models of leukemia
- PMID: 35441749
- PMCID: PMC9277408
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.15376
Immunomodulatory and direct activities of ropeginterferon alfa-2b on cancer cells in mouse models of leukemia
Abstract
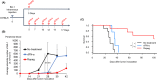
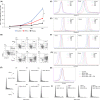
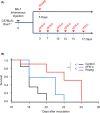
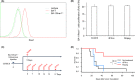
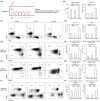
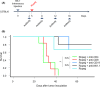
Although ropeginterferon alfa-2b has recently been clinically applied to myeloproliferative neoplasms with promising results, its antitumor mechanism has not been thoroughly investigated. Using a leukemia model developed in immunocompetent mice, we evaluated the direct cytotoxic effects and indirect effects induced by ropeginterferon alfa-2b in tumor cells. Ropeginterferon alfa-2b therapy significantly prolonged the survival of mice bearing leukemia cells and led to long-term remission in some mice. Alternatively, conventional interferon-alpha treatment slightly extended the survival and all mice died. When ropeginterferon alfa-2b was administered to interferon-alpha receptor 1-knockout mice after the development of leukemia to verify the direct effect on the tumor, the survival of these mice was slightly prolonged; nevertheless, all of them died. In vivo CD4+ or CD8+ T-cell depletion resulted in a significant loss of therapeutic efficacy in mice. These results indicate that the host adoptive immunostimulatory effect of ropeginterferon alfa-2b is the dominant mechanism through which tumor cells are suppressed. Moreover, mice in long-term remission did not develop leukemia, even after tumor rechallenge. Rejection of rechallenge tumors was canceled only when both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells were removed in vivo, which indicates that each T-cell group functions independently in immunological memory. We show that ropeginterferon alfa-2b induces excellent antitumor immunomodulation in hosts. Our finding serves in devising therapeutic strategies with ropeginterferon alfa-2b.
Keywords: adoptive immunity; antitumor effector cells; immunomodulatory effect; interferon-alpha; ropeginterferon alfa-2b.
© 2022 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A pharmacokinetic evaluation of ropeginterferon alfa-2b in the treatment of polycythemia vera.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021 Jan;17(1):3-7. doi: 10.1080/17425255.2021.1839050. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33118413 Review.
-
ROP-ET: a prospective phase III trial investigating the efficacy and safety of ropeginterferon alfa-2b in essential thrombocythemia patients with limited treatment options.Ann Hematol. 2024 Jul;103(7):2299-2310. doi: 10.1007/s00277-024-05665-4. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Ann Hematol. 2024. PMID: 38438627 Free PMC article.
-
Ropeginterferon alfa-2b versus standard therapy for polycythaemia vera (PROUD-PV and CONTINUATION-PV): a randomised, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial and its extension study.Lancet Haematol. 2020 Mar;7(3):e196-e208. doi: 10.1016/S2352-3026(19)30236-4. Epub 2020 Jan 31. Lancet Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32014125 Clinical Trial.
-
Exposure-efficacy and exposure-safety analyses of ropeginterferon alfa-2b treatment in patients with polycythaemia vera.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;90(6):1493-1502. doi: 10.1111/bcp.16043. Epub 2024 Mar 19. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38500445 Clinical Trial.
-
Ropeginterferon alfa-2b for the treatment of patients with polycythemia vera.Drugs Today (Barc). 2020 Mar;56(3):195-202. doi: 10.1358/dot.2020.56.3.3107706. Drugs Today (Barc). 2020. PMID: 32282866 Review.
References
-
- Sistigu A, Yamazaki T, Vacchelli E, et al. Cancer cell‐autonomous contribution of type I interferon signaling to the efficacy of chemotherapy. Nat Med. 2014;20(11):1301‐1309. - PubMed
-
- Anguille S, Lion E, Willemen Y, Van Tendeloo VF, Berneman ZN, Smits EL. Interferon‐α in acute myeloid leukemia: an old drug revisited. Leukemia. 2011;25(5):739‐748. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

