Th2 Cytokines IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10 Promote Differentiation of Pro-Lymphatic Progenitors Derived from Bone Marrow Myeloid Precursors
- PMID: 35442077
- PMCID: PMC9232236
- DOI: 10.1089/scd.2022.0004
Th2 Cytokines IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10 Promote Differentiation of Pro-Lymphatic Progenitors Derived from Bone Marrow Myeloid Precursors
Abstract
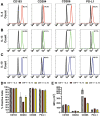
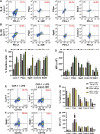
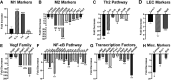
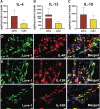
Myeloid-lymphatic endothelial cell progenitors (M-LECP) are a subset of bone marrow (BM)-derived cells characterized by expression of M2-type macrophage markers. We previously showed significant contribution of M-LECP to tumor lymphatic formation and metastasis in human clinical breast tumors and corresponding mouse models. Since M2 type is induced in macrophages by immunosuppressive Th2 cytokines IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10, we hypothesized that these factors might promote pro-lymphatic specification of M-LECP during their differentiation from BM myeloid precursors. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed expression of Th2 cytokines and their receptors in mouse BM cells under conditions leading to M-LECP differentiation, namely, CSF-1 treatment followed by activation of TLR4. We found that under these conditions, all three Th2 receptors were strongly upregulated in >95% of the cells that also secrete endogenous IL-10, but not IL-4 or IL-13 ligands. However, addition of any of the Th2 factors to CSF-1 primed cells significantly increased generation of myeloid-lymphatic progenitors as indicated by co-induction of lymphatic-specific (eg, Lyve-1, integrin-a9, collectin-12, and stabilin-1) and M2-type markers (eg, CD163, CD204, CD206, and PD-L1). Antibody-mediated blockade of either IL-10 receptor (IL-10R) or IL-10 ligand significantly reduced both immunosuppressive and lymphatic phenotypes. Moreover, tumor-recruited Lyve-1+ lymphatic progenitors in vivo expressed all Th2 receptors as well as corresponding ligands, including IL-4 and IL-13, which were absent in BM cells. This study presents original evidence for the significant role of Th2 cytokines in co-development of immunosuppressive and lymphatic phenotypes in tumor-recruited M2-type myeloid cells. Progenitor-mediated increase in lymphatic vessels can enhance immunosuppression by physical removal of stimulatory immune cells. Thus, targeting Th2 pathways might simultaneously relieve immunosuppression and inhibit differentiation of pro-lymphatic progenitors that ultimately promote tumor spread.
Keywords: Th2 cytokines; lymphangiogenesis; lymphatic endothelial progenitors; myeloid cell differentiation.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tumor microenvironment restricts IL-10 induced multipotent progenitors to myeloid-lymphatic phenotype.PLoS One. 2024 Apr 19;19(4):e0298465. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0298465. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38640116 Free PMC article.
-
Lymphatic Endothelial Cell Progenitors in the Tumor Microenvironment.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1234:87-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-37184-5_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32040857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic endothelial progenitors originate from plastic myeloid cells activated by toll-like receptor-4.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 9;12(6):e0179257. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179257. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28598999 Free PMC article.
-
Bone Marrow Myeloid-Lymphatic Progenitors Expand Tumor Lymphatic Vasculature Through Cell Fusion.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 28;17(11):1804. doi: 10.3390/cancers17111804. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40507286 Free PMC article.
-
Novel role of immature myeloid cells in formation of new lymphatic vessels associated with inflammation and tumors.J Leukoc Biol. 2017 Aug;102(2):253-263. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1MR1016-434RR. Epub 2017 Apr 13. J Leukoc Biol. 2017. PMID: 28408396 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune Response Modulation by HPV16 Oncoproteins in Lung Cancer: Insights from Clinical and In Vitro Investigations.Viruses. 2024 Nov 4;16(11):1731. doi: 10.3390/v16111731. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 39599846 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory and anti-rejection effects of herbal medicine ingredients in organ transplantation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1568988. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1568988. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40539066 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of neuroimmune cytokine networks by antidepressants: implications in mood regulation.Transl Psychiatry. 2025 Aug 23;15(1):314. doi: 10.1038/s41398-025-03532-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40849324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lncrna NEAT1 Regulates Th1/Th2 in Pediatric Asthma by Targeting MicroRNA-217/GATA3.Iran J Public Health. 2023 Jan;52(1):106-117. doi: 10.18502/ijph.v52i1.11671. Iran J Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36824247 Free PMC article.
-
Autistic spectrum disorder (ASD) - Gene, molecular and pathway signatures linking systemic inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, transsynaptic signalling, and neurodevelopment.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023 Jun 5;30:100646. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2023.100646. eCollection 2023 Jul. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2023. PMID: 37334258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alitalo K. (2011). The lymphatic vasculature in disease. Nat Med 17:1371–1380. - PubMed
-
- Tan KW, Chong SZ and Angeli V. (2014). Inflammatory lymphangiogenesis: cellular mediators and functional implications. Angiogenesis 17:373–381. - PubMed
-
- Al-Rawi MA and Jiang WG. (2011). Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Front Biosci 16:723–739. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
