UBR5 is a novel regulator of WNK1 stability
- PMID: 35442829
- PMCID: PMC9169826
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00417.2021
UBR5 is a novel regulator of WNK1 stability
Abstract
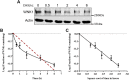
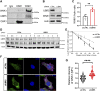
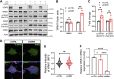
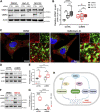
The with no lysine (K) 1 (WNK1) protein kinase maintains cellular ion homeostasis in many tissues through actions on ion cotransporters and channels. Increased accumulation of WNK1 protein leads to pseudohypoaldosteronism type II (PHAII), a form of familial hypertension. WNK1 can be degraded via its adaptor-dependent recruitment to the Cullin3-RBX1 E3 ligase complex by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Disruption of this process also leads to disease. To determine if this is the primary mechanism of WNK1 turnover, we examined WNK1 protein stability and degradation by measuring its rate of decay after blockade of translation. Here, we show that WNK1 protein degradation exhibits atypical kinetics in HeLa cells. Consistent with this apparent complexity, we found that multiple degradative pathways can modulate cellular WNK1 protein amount. WNK1 protein is degraded by not only the proteasome but also the lysosome. Non-lysosomal cysteine proteases calpain and caspases also influence WNK1 degradation, as inhibitors of these proteases modestly increased WNK1 protein expression. Importantly, we discovered that the E3 ubiquitin ligase UBR5 interacts with WNK1 and its deficiency results in increased WNK1 protein. Our results further demonstrate that increased WNK1 in UBR5-depleted cells is attributable to reduced lysosomal degradation of WNK1 protein. Taken together, our findings provide insights into the multiplicity of degradative pathways involved in WNK1 turnover and uncover UBR5 as a previously unknown regulator of WNK1 protein stability that leads to lysosomal degradation of WNK1 protein.
Keywords: UBR5; WNK1; proteolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Impaired degradation of WNK1 and WNK4 kinases causes PHAII in mutant KLHL3 knock-in mice.Hum Mol Genet. 2014 Oct 1;23(19):5052-60. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu217. Epub 2014 May 12. Hum Mol Genet. 2014. PMID: 24821705
-
WNK1 activates SGK1 to regulate the epithelial sodium channel.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Jul 19;102(29):10315-20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504422102. Epub 2005 Jul 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16006511 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of NCC and NKCC2 cotransporters by kidney-specific WNK1 revealed by gene disruption and transgenic mouse models.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Mar 1;20(5):855-66. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq525. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Hum Mol Genet. 2011. PMID: 21131289 Free PMC article.
-
WNK1 in the kidney.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2022 Sep 1;31(5):471-478. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000820. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35894282 Review.
-
Kelch-like 3/Cullin 3 ubiquitin ligase complex and WNK signaling in salt-sensitive hypertension and electrolyte disorder.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016 Sep;31(9):1417-24. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfv259. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26152401 Review.
Cited by
-
WNK1 in Malignant Behaviors: A Potential Target for Cancer?Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 22;10:935318. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.935318. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35813203 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UBR-5 and UBE2D mediate timely exit from stem fate via destabilization of poly(A)-binding protein PABP-2 in cell state transition.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Oct 22;121(43):e2407561121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2407561121. Epub 2024 Oct 15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39405353 Free PMC article.
-
SMURF1/2 are novel regulators of WNK1 stability.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 16:2024.07.31.606092. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.31.606092. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39131382 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

