Changes in orthopaedic operating theatre practice, monitored using settle plates
- PMID: 35442847
- PMCID: PMC9433170
- DOI: 10.1308/rcsann.2021.0328
Changes in orthopaedic operating theatre practice, monitored using settle plates
Abstract
Introduction: The importance of ultraclean air in reducing deep infection was studied by Charnley who showed that the rate decreased as the airborne bacterial load was reduced. The effectiveness was shown in a large Medical Research Council (MRC) trial, but registry data have not shown a consistent benefit. Because we treat patients with rheumatoid arthritis, we decided to look at our theatre air quality.
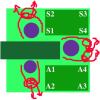
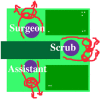
Methods: In phase 1 we monitored air quality using settle plates, exposed for one hour after the incision, on the instrument trolleys in a joint replacement theatre. In phase 1 the scrub person did not wear a body exhaust system. In phase 2 all three staff used a body exhaust system, and we played close attention to the orientation and position of the surgical lights and trolleys.
Results: In phase 1 we grew 0.24 colonies/plate/hour in the ultraclean zone, which is comparable to the Charnley trial findings. In the second phase we grew 0.03 colonies/plate/hour (p<0.001). When plates were placed on the trolleys in controlled positions there was a tendency for the colonies to appear on the corners of the trolleys at the edge of the clean zone (NS).
Discussion: The study showed that in phase 1 colony counts comparable to the original Charnley studies were achieved. Colony counts of 0.03 colonies/plate/hour can be achieved in contemporary practice, with all team members using body exhausts.
Keywords: Infection; Joint replacement; Operating theatre; Settle plates.
Figures
References
-
- Charnley J. Postoperative infection after total hip replacement with special reference to air contamination in the operating room. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1972; 87: 167–187. - PubMed
-
- Whyte W, Hodgson R, Tinkler J. The importance of airborne bacterial contamination of wounds. J Hosp Infect 1982; 3: 123–135. - PubMed
-
- Lidwell OM, Lowbury EJ, Whyte Wet al. Airborne contamination of wounds in joint replacement operations: the relationship to sepsis rates. J Hosp Infect 1983; 4: 111–131. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

