Effect of intrinsic foot muscles training on foot function and dynamic postural balance: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 35442981
- PMCID: PMC9020712
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266525
Effect of intrinsic foot muscles training on foot function and dynamic postural balance: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
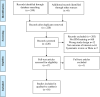
This systematic review aimed to analyse the effects of intrinsic foot muscle (IFM) training on foot function and dynamic postural balance. Keywords related to IFM training were used to search four databases (PubMed, CINAHL, SPORTDiscus and Web of Science databases.) for relevant studies published between January 2011 and February 2021. The methodological quality of the intervention studies was assessed independently by two reviewers by using the modified Downs and Black quality index. Publication bias was also assessed on the basis of funnel plots. This study was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42021232984). Sixteen studies met the inclusion criteria (10 with high quality and 6 with moderate quality). Numerous biomechanical variables were evaluated after IFM training intervention. These variables included IFM characteristics, medial longitudinal arch morphology and dynamic postural balance. This systematic review demonstrated that IFM training can exert positive biomechanical effects on the medial longitudinal arch, improve dynamic postural balance and act as an important training method for sports enthusiasts. Future studies should optimise standardised IFM training methods in accordance with the demands of different sports.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Comment in
-
Editorial Note: Effect of intrinsic foot muscles training on foot function and dynamic postural balance: A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 12;20(8):e0330111. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0330111. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40794605 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Dose-Response Relationships of Resistance Training in Healthy Old Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1693-720. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0385-9. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26420238 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Measures of Balance and Lower-Extremity Muscle Strength/Power in Healthy Individuals Across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1671-92. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0390-z. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26412212 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Supervised vs. Unsupervised Training Programs on Balance and Muscle Strength in Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2017 Nov;47(11):2341-2361. doi: 10.1007/s40279-017-0747-6. Sports Med. 2017. PMID: 28573401
-
Effects of Strength Training Using Unstable Surfaces on Strength, Power and Balance Performance Across the Lifespan: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1645-69. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0384-x. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26359066 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Balance Training on Balance Performance in Healthy Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Sports Med. 2015 Dec;45(12):1721-38. doi: 10.1007/s40279-015-0375-y. Sports Med. 2015. PMID: 26325622 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of intrinsic foot muscle morphology and isometric strength among runners with different strike patterns.PLoS One. 2023 Jun 2;18(6):e0286645. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286645. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37267296 Free PMC article.
-
Local and non-local effects (on the posterior chain) of four weeks of foot exercises: a randomized controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 23;14(1):22000. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71585-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39317709 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gluteus medius muscle strengthening exercise effects on medial longitudinal arch height in individuals with flexible flatfoot: a randomized controlled trial.J Exerc Rehabil. 2023 Feb 23;19(1):57-66. doi: 10.12965/jer.2244572.286. eCollection 2023 Feb. J Exerc Rehabil. 2023. PMID: 36910682 Free PMC article.
-
Utilising Xsens Gait Analysis to Improve Functional Outcomes in Chronic Ankle Instability: A Multifaceted Physiotherapy Approach.Cureus. 2024 Sep 7;16(9):e68880. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68880. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39376853 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of integrated intrinsic foot muscle exercise with foot core training device on balance and body composition among community-dwelling adults aged 60 and above.BMC Geriatr. 2024 May 7;24(1):403. doi: 10.1186/s12877-024-04945-y. BMC Geriatr. 2024. PMID: 38714957 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

