Intramuscular AZD7442 (Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab) for Prevention of Covid-19
- PMID: 35443106
- PMCID: PMC9069994
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2116620
Intramuscular AZD7442 (Tixagevimab-Cilgavimab) for Prevention of Covid-19
Abstract
Background: The monoclonal-antibody combination AZD7442 is composed of tixagevimab and cilgavimab, two neutralizing antibodies against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) that have an extended half-life and have been shown to have prophylactic and therapeutic effects in animal models. Pharmacokinetic data in humans indicate that AZD7442 has an extended half-life of approximately 90 days.
Methods: In an ongoing phase 3 trial, we enrolled adults (≥18 years of age) who had an increased risk of an inadequate response to vaccination against coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), an increased risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2, or both. Participants were randomly assigned in a 2:1 ratio to receive a single dose (two consecutive intramuscular injections, one containing tixagevimab and the other containing cilgavimab) of either 300 mg of AZD7442 or saline placebo, and they were followed for up to 183 days in the primary analysis. The primary safety end point was the incidence of adverse events after a single dose of AZD7442. The primary efficacy end point was symptomatic Covid-19 (SARS-CoV-2 infection confirmed by means of reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction assay) occurring after administration of AZD7442 or placebo and on or before day 183.
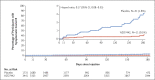
Results: A total of 5197 participants underwent randomization and received one dose of AZD7442 or placebo (3460 in the AZD7442 group and 1737 in the placebo group). The primary analysis was conducted after 30% of the participants had become aware of their randomized assignment. In total, 1221 of 3461 participants (35.3%) in the AZD7442 group and 593 of 1736 participants (34.2%) in the placebo group reported having at least one adverse event, most of which were mild or moderate in severity. Symptomatic Covid-19 occurred in 8 of 3441 participants (0.2%) in the AZD7442 group and in 17 of 1731 participants (1.0%) in the placebo group (relative risk reduction, 76.7%; 95% confidence interval [CI], 46.0 to 90.0; P<0.001); extended follow-up at a median of 6 months showed a relative risk reduction of 82.8% (95% CI, 65.8 to 91.4). Five cases of severe or critical Covid-19 and two Covid-19-related deaths occurred, all in the placebo group.
Conclusions: A single dose of AZD7442 had efficacy for the prevention of Covid-19, without evident safety concerns. (Funded by AstraZeneca and the U.S. government; PROVENT ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT04625725.).
Copyright © 2022 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
Monoclonal Antibodies with Extended Half-Life to Prevent Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2022 Jun 9;386(23):2236-2238. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe2205563. N Engl J Med. 2022. PMID: 35675183 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
In persons at risk for poor vaccination response or COVID-19 exposure, tixagevimab + cilgavimab reduced COVID-19.Ann Intern Med. 2022 Aug;175(8):JC92. doi: 10.7326/J22-0056. Epub 2022 Aug 2. Ann Intern Med. 2022. PMID: 35914259
References
-
- Haas EJ, Angulo FJ, McLaughlin JM, et al. Impact and effectiveness of mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 cases, hospitalisations, and deaths following a nationwide vaccination campaign in Israel: an observational study using national surveillance data. Lancet 2021;397:1819-1829. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nasreen S, Chung H, He S, et al. Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe outcomes with variants of concern in Ontario. Nat Microbiol 2022;7(3):379-385. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
