An adult-stage transcriptional program for survival of serotonergic connectivity
- PMID: 35443166
- PMCID: PMC9109281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110711
An adult-stage transcriptional program for survival of serotonergic connectivity
Abstract
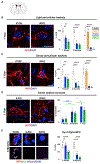
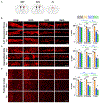
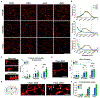
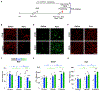
Neurons must function for decades of life, but how these non-dividing cells are preserved is poorly understood. Using mouse serotonin (5-HT) neurons as a model, we report an adult-stage transcriptional program specialized to ensure the preservation of neuronal connectivity. We uncover a switch in Lmx1b and Pet1 transcription factor function from controlling embryonic axonal growth to sustaining a transcriptomic signature of 5-HT connectivity comprising functionally diverse synaptic and axonal genes. Adult-stage deficiency of Lmx1b and Pet1 causes slowly progressing degeneration of 5-HT synapses and axons, increased susceptibility of 5-HT axons to neurotoxic injury, and abnormal stress responses. Axon degeneration occurs in a die back pattern and is accompanied by accumulation of α-synuclein and amyloid precursor protein in spheroids and mitochondrial fragmentation without cell body loss. Our findings suggest that neuronal connectivity is transcriptionally protected by maintenance of connectivity transcriptomes; progressive decay of such transcriptomes may contribute to age-related diseases of brain circuitry.
Keywords: CP: Neuroscience; Lmx1b; Pet1; amyloid precursor protein; axon degeneration; axonopathy; serotonergic connectivity; spheroids; synapse maintenance; transcription factor; α-synuclein.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Transcriptional preservation of serotonergic connectivity may shed light on neurodegeneration.Trends Neurosci. 2022 Aug;45(8):563-565. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2022.05.004. Epub 2022 May 24. Trends Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35624030
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

