GDF15 Suppresses Lymphoproliferation and Humoral Autoimmunity in a Murine Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
- PMID: 35443244
- PMCID: PMC9801254
- DOI: 10.1159/000523991
GDF15 Suppresses Lymphoproliferation and Humoral Autoimmunity in a Murine Model of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Abstract
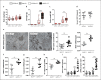
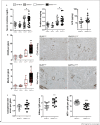
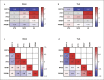
Growth and differentiation factor 15 (GDF15), a divergent member of the transforming growth factor-β superfamily, has been associated with acute and chronic inflammatory conditions including autoimmune disease, i.e., type I diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis. Still, its role in systemic autoimmune disease remains elusive. Thus, we studied GDF15-deficient animals in Fas-receptor intact (C57BL/6) or deficient (C57BL/6lpr/lpr) backgrounds. Further, lupus nephritis (LN) microdissected kidney biopsy specimens were analyzed to assess the involvement of GDF15 in human disease. GDF15-deficiency in lupus-prone mice promoted lymphoproliferation, T-, B- and plasma cell-expansion, a type I interferon signature, and increased serum levels of anti-DNA autoantibodies. Accelerated systemic inflammation was found in association with a relatively mild renal phenotype. Splenocytes of phenotypically overall-normal Gdf15-/- C57BL/6 and lupus-prone C57BL/6lpr/lpr mice displayed increased in vitro lymphoproliferative responses or interferon-dependent transcription factor induction in response to the toll-like-receptor (TLR)-9 ligand CpG, or the TLR-7 ligand Imiquimod, respectively. In human LN, GDF15 expression was downregulated whereas type I interferon expression was upregulated in glomerular- and tubular-compartments versus living donor controls. These findings demonstrate that GDF15 regulates lupus-like autoimmunity by suppressing lymphocyte-proliferation and -activation. Further, the data indicate a negative regulatory role for GDF15 on TLR-7 and -9 driven type I interferon signaling in effector cells of the innate immune system.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; Autoimmunity; Growth and differentiation factor 15; Inflammation; Lupus nephritis; Macrophages; Toll-like-receptor.
© 2022 The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016 Jun 16;2:16039. - PubMed
-
- Anders HJ, Saxena R, Zhao MH, Parodis I, Salmon JE, Mohan C. Lupus nephritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2020 Jan 23;6((1)):7. - PubMed
-
- Breit SN, Tsai VW, Brown DA. Targeting obesity and cachexia: identification of the GFRAL receptor-MIC-1/GDF15 pathway. Trends Mol Med. 2017 Dec;23((12)):1065–7. - PubMed
-
- McPherron AC, Lee SJ. The transforming growth factor β superfamily. In: Leroith D, Bondy C, editors. Growth factors and cytokines in health and disease. JAI; 1996. pp. p. 357–93.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

