COVID-19 infection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia over 15 months of the pandemic. A Campus ALL report
- PMID: 35443561
- PMCID: PMC9335088
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2021.280289
COVID-19 infection in acute lymphoblastic leukemia over 15 months of the pandemic. A Campus ALL report
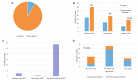
Figures
References
-
- Passamonti F, Cattaneo C, Arcaini L, et al. ; ITA-HEMA-COV Investigators. Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity in patients with haematological malignancies in Italy: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7(10):e737-e745. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Girmenia C, Gentile G, Micozzi A, et al. . COVID-19 in patients with hematologic disorders undergoing therapy: perspective of a large referral hematology center in Rome. Acta Haematol. 2020;143(6):574-582. - PubMed

