A training for health care workers to integrate hepatitis B care and treatment into routine HIV care in a high HBV burden, poorly resourced region of Uganda: the '2for1' project
- PMID: 35443646
- PMCID: PMC9020110
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-022-03329-3
A training for health care workers to integrate hepatitis B care and treatment into routine HIV care in a high HBV burden, poorly resourced region of Uganda: the '2for1' project
Abstract
Introduction: The "2for1" project is a demonstration project to examine the feasibility and effectiveness of HBV care integrated into an HIV clinic and service. An initial phase in implementation of this project was the development of a specific training program. Our objective was to describe key features of this integrated training curriculum and evaluation of its impact in the initial cohort of health care workers (HCWs).
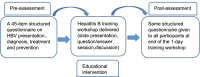
Methods: A training curriculum was designed by experts through literature review and expert opinion. Key distinctive features of this training program (compared to standard HBV training provided in the Government program) were; (i) Comparison of commonalities between HIV and HBV (ii) Available clinic- and community-level infrastructure, and the need to strengthen HBV care through integration (iii) Planning and coordination of sustained service integration. The training was aided by a power-point guided presentation, question and answer session and discussion, facilitated by physicians and hepatologists with expertise in viral hepatitis. Assessment approach used a self-administered questionnaire among a cohort of HCWs from 2 health facilities to answer questions on demographic information, knowledge and attitudes related to HBV and its prevention, before and after the training. Knowledge scores were generated and compared using paired t- tests.
Results: A training curriculum was developed and delivered to a cohort of 44 HCWs including medical and nursing staff from the two project sites. Of the 44 participants, 20 (45.5%) were male, average age (SD) was 34.3 (8.3) with an age range of 22-58 years. More than half (24, 54.5%) had been in service for fewer than 5 years. Mean correct knowledge scores increased across three knowledge domains (HBV epidemiology and transmission, natural history and treatment) post-intervention. However, knowledge related to diagnosis and prevention of HBV did not change.
Conclusion: A structured HBV education intervention conducted as part of an HIV/HBV care integration training for health care workers yielded improved knowledge on HBV and identified aspects that require further training. This approach may be replicated in other settings, as a public health strategy to heighten HBV elimination efforts.
Keywords: Health care workers; Hepatitis B; Knowledge; Uganda.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures
References
-
- Progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections 2019. Accountability for the global health sector strategies, 2016–2021. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019 (WHO/CDS/HIV/19.7).
-
- World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report 2017. 2017. Available from https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/255016.
-
- Akinyemiju T, Abera S, Ahmed M, Alam N, Alemayohu MA, Allen C, et al. The burden of primary liver cancer and underlying etiologies from 1990 to 2015 at the global, regional, and national level: results from the global burden of disease study 2015. JAMA Oncol. 2017;3(12):1683–1691. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.3055. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical