Seroconversion panels demonstrate anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody development after administration of the mRNA-1273 vaccine
- PMID: 35443917
- PMCID: PMC8989688
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2022.04.006
Seroconversion panels demonstrate anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody development after administration of the mRNA-1273 vaccine
Abstract
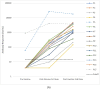
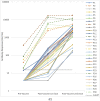
Seroconversion panels are an important tool for investigating antibody responses in acute and chronic phases of disease and development of serological assays for viral diseases including COVID-19. Globally it is anticipated that vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 will facilitate control of the current pandemic. The two COVID-19 seroconversion panels analyzed in this study were obtained from healthcare workers with samples collected before vaccination with the mRNA-1273 vaccine (Moderna) and after the first and second doses of the vaccine. Panel samples were tested for antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 (IgG). Individual subjects with a positive response for anti-SARS-CoV2 IgG in their pre-vaccination samples showed a significantly enhanced response to the first vaccination. In older subjects, lower immunological responses to the first injection were observed, which were overcome by the second injection. All subjects in the study were positive for anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG after the second dose of vaccine.
Keywords: COVID-19; Immunity; Immunoglobulins; SARS-CoV-2; Seroconversion panel; mRNA-1273 vaccine.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Francisco Belda, Oscar Mora, Monica Lopez Martinez and Nerea Torres are employees of Grifols. Rebecca Christie and Michael Crowlet are employees of Access Biologicals..
Figures


References
-
- Johns Hopkins University Center for Systems Science and Engineering. COVID-19 Dashboard. Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Coronavirus Resource Center. Available at: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/. [accessed 10 February 2022].
-
- Diasorin SpA. Liaison SARS-CoV-2 S1/S2 IgG: The full automated serology test for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 IgG antibodies. Available at: https://www.diasorin.com/sites/default/files/allegati/liaisonr_sars-cov-.... [accessed 5 January 2022].
-
- Lopez Martinez M., Ruiz-Arguello B., Torres N., Catarino S., Apraiz I., Maguregui A., et al. Anti-SARS-CoV-2 (immunoglobulin G) ELISA kit, a sensitive and specific assay for the detection of human anti-SARS-CoV-2 immunoglobulin G antibodies. Vox Sang. 2020;115(suppl 1):387.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

