Bempegaldesleukin plus nivolumab in first-line renal cell carcinoma: results from the PIVOT-02 study
- PMID: 35444058
- PMCID: PMC9021810
- DOI: 10.1136/jitc-2021-004419
Bempegaldesleukin plus nivolumab in first-line renal cell carcinoma: results from the PIVOT-02 study
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitor-based combinations have expanded the treatment options for patients with renal cell carcinoma (RCC); however, tolerability remains challenging. The aim of this study was to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the immunostimulatory interleukin-2 cytokine prodrug bempegaldesleukin (BEMPEG) plus nivolumab (NIVO) as first-line therapy in patients with advanced clear-cell RCC.
Methods: This was an open-label multicohort, multicenter, single-arm phase 1/2 study; here, we report results from the phase 1/2 first-line RCC cohort (N=49). Patients received BEMPEG 0.006 mg/kg plus NIVO 360 mg intravenously every 3 weeks. The primary objectives were safety and objective response rate (ORR; patients with measurable disease at baseline and at least one postbaseline tumor response assessment). Secondary objectives included overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS). Exploratory biomarker analyses: association between baseline biomarkers and ORR.
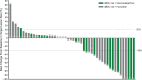
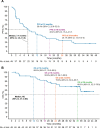
Results: At a median follow-up of 32.7 months, the ORR was 34.7% (17/49 patients); 3/49 patients (6.1%) had a complete response. Of the 17 patients with response, 14 remained in response for >6 months, and 6 remained in response for >24 months. Median PFS was 7.7 months (95% CI 3.8 to 13.9), and median OS was not reached (95% CI 37.3 to not reached). Ninety-eight per cent (48/49) of patients experienced ≥1 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE) and 38.8% (19/49) had grade 3/4 TRAEs, most commonly syncope (8.2%; 4/49) and increased lipase (6.1%; 3/49). No association between exploratory biomarkers and ORR was observed. Limitations include the small sample size and single-arm design.
Conclusions: BEMPEG plus NIVO showed preliminary antitumor activity as first-line therapy in patients with advanced clear-cell RCC and was well tolerated. These findings warrant further investigation.
Keywords: Drug Therapy, Combination; Immunotherapy; Kidney Neoplasms.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2022. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: AOS-R received research funding from BioClin Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Michael and Sherry Sutton Fund for Urothelial Cancer, Nektar Therapeutics, US National Institutes of Health, and Takeda. She has also served as an advisor/consultant to AstraZeneca, Bavarian Nordic, BioClin Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Genentech, Inovio Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Merck, US National Comprehensive Cancer Network, Nektar Therapeutics, and Seattle Genetics. DCC has received consulting fees from Pfizer, Nectar, Torque, and Puretech. AD has been an advisory board member for Nektar Therapeutics. MS has served as a consultant/advisor for Genentech-Roche, Bristol Myers Squibb, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Pfizer, Novartis, Kyowa-Kirin, Amgen, Merus, Seattle Genetics, Immune Design, Prometheus, Anaeropharma, Astellas-Agensys, Immunova, Nektar Therapeutics, Neostem, Pierre-Fabre, Eli Lilly, Symphogen, Lion Biotechnologies, Amphivena, and Adaptive Biotechnologies. MAB has acted as a paid consultant for, and/or as a member of the advisory boards of, Exelixis, Bayer, BMS, Eisai, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Janssen, Genomic Health, Nektar Therapeutics, and Sanofi and has received grants to his institution from Xencor, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Genentech/Roche, Seattle Genetics, Incyte, Nektar Therapeutics, AstraZeneca, Tricon Pharmaceuticals, Peleton Therapeutics, and Pfizer for work performed as outside of the current study. AVB has received institutional research funding from AstraZeneca/MedImmune, F Hoffmann–La Roche/Genentech, Merck, and Seattle Genetics; and honoraria from AstraZeneca/MedImmune, F Hoffmann–La Roche/Genentech and Merck. He has also served as an advisor/consultant to AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Cerulean Pharma, F Hoffmann–La Roche/Genentech, Incyte, Merck, Nektar Therapeutics, Pfizer/EMD Serono, and Seattle Genetics/Astellas. GG has received grants and personal fees from PharmaMar, grants from Novartis, and personal fees from Lilly, Pfizer, Bayer, and Eisai, outside the submitted work. EP, LT, DC, UH, AC, and DY are employees of, and have ownership interest (eg, stock) in, Nektar Therapeutics. SLC is a former employee of, and has ownership interest (eg, stock) in, Nektar Therapeutics. MAT is the chief medical officer at Nektar Therapeutics and has ownership interest (eg, stock) in the company. JZ is the chief research and development officer at Nektar Therapeutics and has ownership interest (eg, stock) in the company. MEH has had a consulting or advisory Role with Nektar Therapeutics, Janssen, Crispr Therapeutics, Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene, and Exelixis; and has received research funding from Apexigen, Astellas Pharma, AstraZeneca/MedImmune, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Lilly, Endocyte, Genentech, Genmab, Innocrin Pharma, Iovance Biotherapeutics, Merck, Nektar Therapeutics, Novartis, Pfizer, Progenics, Sanofi/Aventis, Seattle Genetics, Torque, Unum Therapeutics, and Achilles Therapeutics. NMT has received grant support, consulting fees, and honoraria from Bristol Myers Squibb; grant support from Epizyme and Mirati Therapeutics; grant support, consulting fees, and honoraria from, and served on an advisory board for, Exelixis and Novartis; received consulting fees and honoraria from Argos Therapeutics and Pfizer; and received consulting fees and honoraria from, and served on an advisory board for, Eisai, Nektar Therapeutics, and Oncorena.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network . NCCN clinical practice guideline: Kidney Cancer (v4.2021) [Internet]. Available: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail [Accessed 4 Jun 2021].
-
- Powles T, ESMO Guidelines Committee. Electronic address: clinicalguidelines@esmo.org . Recent eUpdate to the ESMO clinical practice guidelines on renal cell carcinoma on cabozantinib and nivolumab for first-line clear cell renal cancer: renal cell carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2021;32:422–3. 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.11.016 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Powles T, Plimack ER, Soulières D, et al. . Pembrolizumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib monotherapy as first-line treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma (KEYNOTE-426): extended follow-up from a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2020;21:1563–73. 10.1016/S1470-2045(20)30436-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
