A Review on Cutaneous and Musculoskeletal Manifestations of CLOVES Syndrome
- PMID: 35444443
- PMCID: PMC9013705
- DOI: 10.2147/CCID.S351637
A Review on Cutaneous and Musculoskeletal Manifestations of CLOVES Syndrome
Abstract
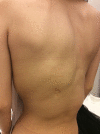
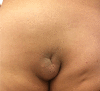
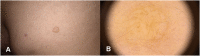
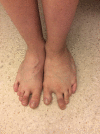
CLOVES syndrome is a novel sporadic mosaic segmental overgrowth syndrome, currently categorized under the canopy of PROS (PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum) disorders. All PROS disorders harbor heterozygous postzygotic activating somatic mutations involving the PIK3CA gene. As an upstream regulator of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signal transduction pathway, activating mutations of PIK3CA gene commence in uncontrolled growth of cutaneous, vascular (capillaries, veins, and lymphatics), adipose, neural, and musculoskeletal tissues. The excessive growth is segmental, patchy, asymmetric, and confined to body parts affected by the mutation. The term 'CLOVES' is an acronym denoting congenital lipomatous overgrowth, vascular malformations, epidermal nevi and spinal (scoliosis) and/ or skeletal anomalies. The syndrome is characterized by an admixture of overgrown tissues, derived mainly from mesoderm and neuroectoderm. Among PROS disorders, CLOVES syndrome represents the extreme end of the spectrum with massive affection of almost the entire body. The syndrome might judiciously be treated with medications hampering with the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signal transduction pathway. This article aims at reviewing the cutaneous and musculoskeletal manifestations of CLOVES syndrome, as the paradigm for PROS disorders. CLOVES syndrome and other PROS disorders are still misdiagnosed, underdiagnosed, underreported, and undertreated by the dermatology community.
Keywords: CLOVES syndrome; PIK3CA-related overgrowth spectrum; cutaneous manifestations; epidermal nevi; lipomas; lymphangiomas; port wine stains.
© 2022 Öztürk Durmaz et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

