Physical Activity Interventions in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 35444485
- PMCID: PMC9015041
- DOI: 10.2147/PHMT.S282611
Physical Activity Interventions in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Introduction: Children with juvenile arthritis (JA) experience pain, stiffness, fatigue, and decreased motion leading to difficulties with daily activities and low physical activity (PA). PA is critical to improve health and function and mitigate JA-associated symptoms. This study evaluated the evidence for PA interventions in children with JA.
Materials and methods: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of PA interventions in children with JA was conducted. Ovid (Medline), Cochrane Library, EMBASE, and CINAHL databases were searched for papers published in English between 1/1/1946 and 9/1/2021. Studies which concurrently assessed medical interventions were excluded. Participant and intervention characteristics and outcomes were extracted. Study internal validity and intervention attributes were assessed.
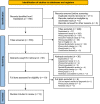
Results: A total of 555 studies were identified, with 13 studies from 10 countries included. Data from 672 children diagnosed with juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) (range of mean ages, 8.7 to 16.1 years) were analyzed. Fifty-two percent of intervention arms incorporated strengthening exercise alone or combined with other exercise, with 61.9% performed 3x/week. About 43.5% of sessions lasted >45 to ≤60 minutes and 65.2% of programs were ≥12 to <28 weeks. PA interventions improved function and symptoms without adverse events. Intervention details were missing especially regarding PA intensity, reasons for dropouts, and adherence. Only two studies incorporated strategies to promote adherence.
Discussion: RCTs of PA interventions in JA only include JIA. Available RCTs used mixed modes of interventions. Reporting of PA interventions lacks sufficient detail to discern the dose-response relationship. Strategies to motivate engagement in PA and to support families to promote PA are lacking, as are studies of long-term outcomes.
Conclusion: There are limited RCTs of PA interventions in JIA. Adherence was better with low intensity programs. PA interventions for JIA yield positive health benefits but better reporting of PA intervention details is needed to generate more high-quality evidence and inform clinical practice.
Prospero registration: Maura Iversen, Johan von Heideken, Marie Andre. Physical Activity in Children with Rheumatic Diseases: a systematic review. PROSPERO 2021 CRD42021274634 Available from: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/display_record.php?ID=CRD42021274634.
Keywords: exercise; juvenile idiopathic arthritis; physical activity.
© 2022 Iversen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no competing interests that could have influenced the conduct of this study.
Figures
References
-
- Petty RE, Southwood TR, Manners P, et al. International league of associations for rheumatology classification of juvenile idiopathic arthritis: second revision, Edmonton, 2001. J Rheumatol. 2004;31(2):390–392. - PubMed
-
- Farpour-Lambert NJ, Keller-Marchand L, Rizzoli R, et al. [Physical exercise and bone development in chronically ill children]. Exercice physique et developpement osseux de l’enfant malade chronique. Rev Méd Suisse. 2004;124(2):73–75. - PubMed
-
- Knops N, Wulffraat N, Lodder S, Houwen R, de Meer K. Resting energy expenditure and nutritional status in children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1999;26(9):2039–2043. - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez-Suarez R, Pistorio A, Cespedes Cruz A, et al. Health-related quality of life of patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis coming from 3 different geographic areas. The PRINTO multinational quality of life cohort study. Rheumatology. 2007;46(2):314–320. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kel218 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources