Molnupiravir and Its Antiviral Activity Against COVID-19
- PMID: 35444647
- PMCID: PMC9013824
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.855496
Molnupiravir and Its Antiviral Activity Against COVID-19
Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) constitutes a major worldwide public health threat and economic burden. The pandemic is still ongoing and the SARS-CoV-2 variants are still emerging constantly, resulting in an urgent demand for new drugs to treat this disease. Molnupiravir, a biological prodrug of NHC (β-D-N(4)-hydroxycytidine), is a novel nucleoside analogue with a broad-spectrum antiviral activity against SARS-CoV, SARS-CoV-2, Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV), influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV), hepatitis C virus (HCV) and Ebola virus (EBOV). Molnupiravir showed potent therapeutic and prophylactic activity against multiple coronaviruses including SARS-CoV-2, SARS-CoV, and MERS-CoV in animal models. In clinical trials, molnupiravir showed beneficial effects for mild to moderate COVID-19 patients with a favorable safety profile. The oral bioavailability and potent antiviral activity of molnupiravir highlight its potential utility as a therapeutic candidate against COVID-19. This review presents the research progress of molnupiravir starting with its discovery and synthesis, broad-spectrum antiviral effects, and antiviral mechanism. In addition, the preclinical studies, antiviral resistance, clinical trials, safety, and drug tolerability of molnupiravir are also summarized and discussed, aiming to expand our knowledge on molnupiravir and better deal with the COVID-19 epidemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antiviral; molnupiravir; orally bioavailable; safety.
Copyright © 2022 Tian, Pang, Li, Lou, An, Zhu, Song, Tong, Fan and Fan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


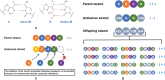

References
-
- Borba M, Val F, Sampaio VS, Alexandre M, Melo GC, Brito M, et al. . Effect of High vs Low Doses of Chloroquine Diphosphate as Adjunctive Therapy for Patients Hospitalized With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) Infection: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw Open (2020) 3(4):e208857. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.8857 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

