Impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on vaccine-induced immune responses over time
- PMID: 35444806
- PMCID: PMC9015077
- DOI: 10.1002/cti2.1388
Impact of SARS-CoV-2 infection on vaccine-induced immune responses over time
Abstract
Objective: To determine the long-term impact of prior SARS-CoV-2 infection on immune responses after COVID-19 vaccination.
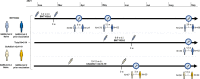
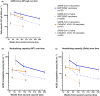
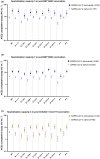
Methods: Using longitudinally collected blood samples from the COMMUNITY study, we determined binding (WHO BAU mL-1) and neutralising antibody titres against ten SARS-CoV-2 variants over 7 months following BNT162b2 in SARS-CoV-2-recovered (n = 118) and SARS-CoV-2-naïve (n = 289) healthcare workers with confirmed prior SARS-CoV-2 infection. A smaller group with (n = 47) and without (n = 60) confirmed prior SARS-CoV-2 infection receiving ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 was followed for 3 months. SARS-CoV-2-specific memory T-cell responses were investigated in a subset of SARS-CoV-2-naïve and SARS-CoV-2-recovered vaccinees.
Results: Vaccination with both vaccine platforms resulted in substantially enhanced T-cell responses, anti-spike IgG responses and neutralising antibodies effective against ten SARS-CoV-2 variants in SARS-CoV-2-recovered participants as compared to SARS-CoV-2-naïve participants. The enhanced immune responses sustained over 7 months following vaccination.
Conclusion: These findings imply that prior SARS-CoV-2 infection should be taken into consideration when planning booster doses and design of current and future COVID-19 vaccine programmes.
Keywords: COVID‐19; SARS‐CoV‐2; hybrid immunity; immune responses; vaccination.
© 2022 The Authors. Clinical & Translational Immunology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Australian and New Zealand Society for Immunology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
SoH has participated in the AstraZeneca COVID‐19 SCG Virtual Advisory Board. Otherwise, the authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
