Relationship between right atrial pressure and the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in patients with advanced heart failure
- PMID: 35444854
- PMCID: PMC8990151
- DOI: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2022.22254
Relationship between right atrial pressure and the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) score in patients with advanced heart failure
Abstract
Background: This study aims to investigate the association between right atrial pressure and the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score and to evaluate the ability of this scoring system to accurately predict the value of right atrial pressure.
Methods: Between April 2016 and November 2018, a total of 137 patients (118 males, 19 females; median age: 49 years; range, 40 to 54 years) with advanced heart failure who were candidates for left ventricular assist device implantation or heart transplantation were retrospectively analyzed. We developed a formula calculated by using the biochemical and cardiac catheterization parameters of the patients.
Results: There was a strong correlation between the right atrial pressure and the scores (r=0.510, p<0.001). The estimated right atrial pressure was calculated as "2 + (0.92 x Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score)" (unstandardized coefficient 0.920, t value 7.674, p<0.001). The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score was found to be an independent predictor of high right atrial pressure (odds ratio=1.491, 95% confidence interval: 1.244-1.786, p<0.001). The calculated area under the curve was 0.789 (95% confidence interval: 0.710-0.867, p<0.001) and the cut-off value of the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score in the prediction of high right atrial pressure was 10.5 with 75% sensitivity and 73% specificity.
Conclusion: We define a method to calculate right atrial pressure obtained by using the Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score without the need for cardiac catheterization during the hospitalization and follow-up period of patients with advanced heart failure.
Keywords: Advanced heart failure; Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Score; right atrial pressure.
Copyright © 2022, Turkish Society of Cardiovascular Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

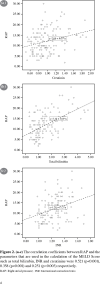
RAP: Right atrial pressure; INR: International normalized ratio
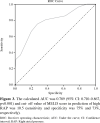
ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; AUC: Under the curve; CI: Confidence interval; RAP: Right atrial pressure.
Similar articles
-
Liver dysfunction assessed by model for end-stage liver disease excluding INR (MELD-XI) scoring system predicts adverse prognosis in heart failure.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 23;9(6):e100618. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0100618. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24955578 Free PMC article.
-
Model of End-Stage Liver Disease-eXcluding International Normalized Ratio (MELD-XI) Scoring System to Predict Outcomes in Patients Who Undergo Left Ventricular Assist Device Implantation.Ann Thorac Surg. 2018 Aug;106(2):513-519. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2018.02.082. Epub 2018 Apr 4. Ann Thorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 29626453
-
[Correlations between MELD score and left ventricular function in patients with end-stage liver disease].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010 Oct;18(10):758-62. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2010.10.009. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21059293 Chinese.
-
Can echocardiographic evaluation of cardiopulmonary hemodynamics decrease right heart catheterizations in end-stage heart failure patients awaiting transplantation?Am J Cardiol. 2010 Dec 1;106(11):1657-62. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2010.07.022. Epub 2010 Oct 14. Am J Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 21094370
-
Ability of King's College Criteria and Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Scores to Predict Mortality of Patients With Acute Liver Failure: A Meta-analysis.Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Apr;14(4):516-525.e5; quiz e43-e45. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.10.007. Epub 2015 Oct 20. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 26499930 Review.
References
-
- Kamath PS, Wiesner RH, Malinchoc M, Kremers W, Therneau TM, Kosberg CL, et al. A model to predict survival in patients with end-stage liver disease. Hepatology. 2001;33:464–470. - PubMed
-
- Costa BP, Sousa FC, Serôdio M, Carvalho C. Value of MELD and MELD-based indices in surgical risk evaluation of cirrhotic patients: Retrospective analysis of 190 cases. World J Surg. 2009;33:1711–1719. - PubMed
-
- Malinchoc M, Kamath PS, Gordon FD, Peine CJ, Rank J, ter Borg PC. A model to predict poor survival in patients undergoing transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts. Hepatology. 2000;31:864–871. - PubMed
-
- Szyguła-Jurkiewicz B, Nadziakiewicz P, Zakliczynski M, Szczurek W, Chraponski J, Zembala M, et al. Predictive value of hepatic and renal dysfunction based on the models for end-stage liver disease in patients with heart failure evaluated for heart transplant. Transplant Proc. 2016;48:1756–1760. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
