Successful method in the treatment of complicated sternal dehiscence and mediastinitis: Sternal reconstruction with osteosynthesis system supported by vacuum-assisted closure
- PMID: 35444857
- PMCID: PMC8990150
- DOI: 10.5606/tgkdc.dergisi.2022.20958
Successful method in the treatment of complicated sternal dehiscence and mediastinitis: Sternal reconstruction with osteosynthesis system supported by vacuum-assisted closure
Abstract
Background: This study aims to evaluate the results of the method we used to treat sternal dehiscence and mediastinitis due to median sternotomy following open heart surgery.
Methods: Between July 2014 and March 2019, a total of 13 patients (8 males, 5 females; mean age: 60.3±2.9 years; range, 33 to 74 years) who underwent sternal reconstruction procedure and developed sternal dehiscence and mediastinitis after cardiac surgery were retrospectively analyzed. Data of the patients were retrieved from the hospital records.
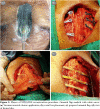
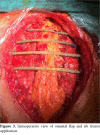
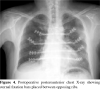
Results: Before the procedure, reconstruction was performed by using the Robiscek technique in three cases and a conventional rewiring technique was used in one case. Except for one case, all the other cases had sternal purulent discharge (n=12, 92%). Except for four cases, all cases had at least two fracture lines in the sternum (n=9, 69%). One to 10 sessions of (median=4) vacuum-assisted closure therapy were used in cases before the procedure. At least two bars were placed between the opposite ribs for sternal fixation. Except for three cases, all of the cases were placed transdiaphragmatic harvested omentum in the sternal cavity. Seroma and local infection recurrence occurred in two cases (n=2, 15.3%) and incisional hernia in one case (n=1, 7.6%). Thoracic stabilization was successfully achieved in all cases.
Conclusion: Thoracic stabilization can be successfully achieved in complicated sternal dehiscence cases with sternal reconstruction with STRATOS system supported by vacuum-assisted closure therapy, until the culture turns negative in the preoperative period and by the use of transdiaphragmatic omentum intraoperatively inside the sternal cavity.
Keywords: Mediastinitis; sternal dehiscence; sternal reconstruction.
Copyright © 2022, Turkish Society of Cardiovascular Surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declared no conflicts of interest with respect to the authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures

References
-
- Voss B, Bauernschmitt R, Will A, Krane M, Kröss R, Brockmann G, et al. Sternal reconstruction with titanium plates in complicated sternal dehiscence. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;34:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Careaga Reyna G, Aguirre Baca GG, Medina Concebida LE, Borrayo Sánchez G, Prado Villegas G, Argüero Sánchez R. Risk factors for mediastinitis and sternal dehiscence after cardiac surgery. Rev Esp Cardiol. 2006;59:130–135. - PubMed
-
- Francel TJ, Kouchoukos NT. A rational approach to wound difficulties after sternotomy: The problem. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72:1411–1418. - PubMed
-
- Risnes I, Abdelnoor M, Almdahl SM, Svennevig JL. Mediastinitis after coronary artery bypass grafting risk factors and long-term survival. Ann Thorac Surg. 2010;89:1502–1509. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
