A Machine Learning Based Framework to Identify and Classify Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Large-Scale Population
- PMID: 35444985
- PMCID: PMC9013842
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.846118
A Machine Learning Based Framework to Identify and Classify Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Large-Scale Population
Abstract
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a common serious health problem worldwide, which lacks efficient medical treatment. We aimed to develop and validate the machine learning (ML) models which could be used to the accurate screening of large number of people. This paper included 304,145 adults who have joined in the national physical examination and used their questionnaire and physical measurement parameters as model's candidate covariates. Absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) was used to feature selection from candidate covariates, then four ML algorithms were used to build the screening model for NAFLD, used a classifier with the best performance to output the importance score of the covariate in NAFLD. Among the four ML algorithms, XGBoost owned the best performance (accuracy = 0.880, precision = 0.801, recall = 0.894, F-1 = 0.882, and AUC = 0.951), and the importance ranking of covariates is accordingly BMI, age, waist circumference, gender, type 2 diabetes, gallbladder disease, smoking, hypertension, dietary status, physical activity, oil-loving and salt-loving. ML classifiers could help medical agencies achieve the early identification and classification of NAFLD, which is particularly useful for areas with poor economy, and the covariates' importance degree will be helpful to the prevention and treatment of NAFLD.
Keywords: LASSO; machine learning; non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); predictive models; screening model.
Copyright © 2022 Ji, Xue, Zhang, Yao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
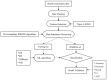
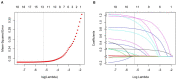
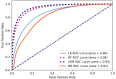
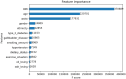
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

