The Biological Functions and Regulatory Mechanisms of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5 in Various Diseases
- PMID: 35445019
- PMCID: PMC9013884
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.857919
The Biological Functions and Regulatory Mechanisms of Fatty Acid Binding Protein 5 in Various Diseases
Abstract
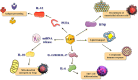
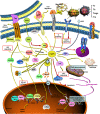
In recent years, fatty acid binding protein 5 (FABP5), also known as fatty acid transporter, has been widely researched with the help of modern genetic technology. Emerging evidence suggests its critical role in regulating lipid transport, homeostasis, and metabolism. Its involvement in the pathogenesis of various diseases such as metabolic syndrome, skin diseases, cancer, and neurological diseases is the key to understanding the true nature of the protein. This makes FABP5 be a promising component for numerous clinical applications. This review has summarized the most recent advances in the research of FABP5 in modulating cellular processes, providing an in-depth analysis of the protein's biological properties, biological functions, and mechanisms involved in various diseases. In addition, we have discussed the possibility of using FABP5 as a new diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for human diseases, shedding light on challenges facing future research.
Keywords: FABP5; cell differentiation; immune response; lipid homeostasis; lipid metabolism; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Chen, Zhan, Marquez, Zhuo, Qi, Zhu, He, Chen, Zhang, Shen, Chen, Gu, Guo, Liu and Xie.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

