Collaborative Development of a PACS-Integrated Quality Control Dashboard: a Single Institutional Experience
- PMID: 35445342
- PMCID: PMC9582052
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-022-00621-y
Collaborative Development of a PACS-Integrated Quality Control Dashboard: a Single Institutional Experience
Abstract
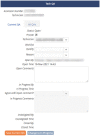
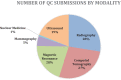
Regular communication between technologists and radiologists is necessary for maintaining optimal diagnostic image quality throughout a radiology practice. In a large hospital system with multiple sites, this task becomes increasingly difficult without simultaneously causing significant disruptions in the clinical workflow and decreased throughput. Thus, establishing a system for quality control reporting that enables effective communication in a seamless and convenient manner is imperative. In this report, we describe the development of a new integrated system, in collaboration with our PACS vendor, with tools that allow for instant reporting of quality errors and dashboards providing real-time up-to-date quality data across our hospital system, directly accessible from PACS. To date, 8,167 quality reports have been logged in our new system with roughly 355 submissions per month. Early user engagement and consensus feedback among radiologists and technologists have been positive suggesting an overall improvement from prior systems. We hope this report can help inform other radiology enterprises seeking to improve quality control reporting within their clinical practice.
Keywords: Communication; PACS; Quality assurance; Quality control; Radiology; Technologist.
© 2022. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Savoie B, Lexa FJ, Nagy P: Radiologist technologist communication. J Am Coll Radiol (10)2: 144–145,2013 - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

