A novel desmoplakin mutation causes dilated cardiomyopathy with palmoplantar keratoderma as an early clinical sign
- PMID: 35445468
- PMCID: PMC9545885
- DOI: 10.1111/jdv.18164
A novel desmoplakin mutation causes dilated cardiomyopathy with palmoplantar keratoderma as an early clinical sign
Abstract
Background: PPKs represent a heterogeneous group of disorders with hyperkeratosis of palmar and/or plantar skin. PPK, hair shaft abnormalities, cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias can be caused by mutations in desmosomal genes, e.g. desmoplakin (DSP). PPK should trigger genetic testing to reveal mutations with possible related cardiac disease.
Objectives: To report a large multigenerational family with a novel DSP mutation associated with early-onset PPK and adult-onset cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias.
Methods: A custom-designed in-house panel of 35 PPK related genes was used to screen mutations in the index patient with focal PPK. The identified DSP mutation was verified by Sanger sequencing. DNA samples from 20 members of the large multigenerational family were sequenced for the DSP mutation. Medical records were reviewed. Clinical dermatological evaluation was performed, including light microscopy of hair samples. Cardiac evaluation included clinical examination, echocardiography, cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (CMR), electrocardiogram (ECG), Holter monitoring and laboratory tests.
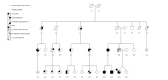
Results: We identified a novel autosomal dominant truncating DSP c.2493delA p.(Glu831Aspfs*33) mutation associated with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) with arrhythmia susceptibility and focal PPK as an early cutaneous sign. The mutation was found in nine affected family members, but not in any unaffected members. Onset of dermatological findings preceded cardiac symptoms which were variable and occurred at adult age.
Conclusions: We report a novel truncating DSP mutation causing focal PPK with varying severity and left ventricular dilatation and ventricular extrasystoles. This finding emphasizes the importance of genetic diagnosis in patients with PPK for clinical counselling and management of cardiomyopathies and arrhythmias.
Keywords: dilated cardiomyopathy; genodermatosis; next-generation sequencing; palmoplantar keratoderma.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Figures

References
-
- Pigors M, Schwieger‐Briel A, Cosgarea R et al. Desmoplakin mutations with palmoplantar keratoderma, woolly hair and cardiomyopathy. Acta Derm Venereol 2015; 95: 337–340. - PubMed
-
- Polivka L, Bodemer C, Hadj‐Rabia S. Combination of palmoplantar keratoderma and hair shaft anomalies, the warning signal of severe arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy: a systematic review on genetic desmosomal diseases. J Med Genet 2016; 53: 289–295. - PubMed
-
- Guerra L, Castori M, Didona B, Castiglia D, Zambruno G. Hereditary palmoplantar keratodermas. Part II: syndromic palmoplantar keratodermas ‐ diagnostic algorithm and principles of therapy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2018; 32: 899–925. - PubMed
-
- Has C, Technau‐Hafsi K. Palmoplantar keratodermas: clinical and genetic aspects. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges 2016; 14: 123–139. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

