Epidemiology of interstitial lung disease in systemic lupus erythematosus in France: A nation-wide population-based study over 10 years
- PMID: 35446457
- PMCID: PMC9540592
- DOI: 10.1111/resp.14268
Epidemiology of interstitial lung disease in systemic lupus erythematosus in France: A nation-wide population-based study over 10 years
Abstract
Background and objective: Data regarding interstitial lung disease (ILD) in the setting of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are limited. We used a nationwide database to determine the incidence and the prevalence of ILD in SLE.
Methods: Characteristics of all SLE inpatients admitted between 2011 and 2012 in France were analysed through the French medico-administrative database. Features associated with the presence of ILD were studied. Cox hazard model was used to measure the impact of ILD on survival from the first stay to 2020. The incidence of ILD in SLE was estimated by analysing the onset of ILD from 2013 to 2020 in SLE patients who had no evidence of ILD in 2013.
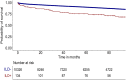
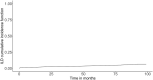
Results: Between 2011 and 2012, 10,460 SLE patients had at least one hospital stay and could be traced until 2020. Among them, 134 (1.2%) had an ILD diagnosed at baseline. The frequency of ILD in SLE was higher in patients who had an associated autoimmune disease such as Sjögren's syndrome or systemic sclerosis (29.9% vs. 5.9%, p < 0.0001). ILD was associated with an increased risk of death in SLE in the multivariable analysis (hazard ratio [95% CI] 1.992 [1.420-2.794]; p < 0.0001). Among the 31,029 SLE patients with no evidence of ILD at baseline, ILD occurred in 795 (2.6%) between 2013 and 2020. The incidence rate of ILD in SLE was 10.26 for 1000 patient-years [95% CI: 10.24-10.28].
Conclusion: In SLE, ILD is exceedingly rare, often associated with another systemic autoimmune disorder and appears as a major risk factor for death.
Keywords: death; epidemiology; interstitial lung disease; systemic lupus erythematosus.
© 2022 The Authors. Respirology published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Asian Pacific Society of Respirology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
Comment in
-
Unravelling the enigma of systemic lupus erythematosus-associated ILD.Respirology. 2022 Aug;27(8):567-568. doi: 10.1111/resp.14298. Epub 2022 Jun 7. Respirology. 2022. PMID: 35672273 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lisnevskaia L, Murphy G, Isenberg D. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. 2014. Nov 22;384(9957):1878–88. - PubMed
-
- Narváez J, Borrell H, Sánchez‐Alonso F, Rúa‐Figueroa I, López‐Longo FJ, Galindo‐Izquierdo M, et al. Primary respiratory disease in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: data from the Spanish rheumatology society lupus registry (RELESSER) cohort. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. Dec;20(1):1–10. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Weinrib L, Sharma OP, Quismorio FP. A long‐term study of interstitial lung disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1990. Aug;20(1):48–56. - PubMed
-
- Haupt HM, Moore GW, Hutchins GM. The lung in systemic lupus erythematosus. Analysis of the pathologic changes in 120 patients. Am J Med. 1981. Nov;71(5):791–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

