Preferential expansion of CD8+ CD19-CAR T cells postinfusion and the role of disease burden on outcome in pediatric B-ALL
- PMID: 35446934
- PMCID: PMC9647829
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021006293
Preferential expansion of CD8+ CD19-CAR T cells postinfusion and the role of disease burden on outcome in pediatric B-ALL
Abstract
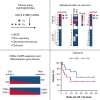
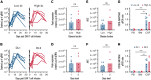
T cells expressing CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptors (CD19-CARs) have potent antileukemia activity in pediatric and adult patients with relapsed and/or refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL). However, not all patients achieve a complete response (CR), and a significant percentage relapse after CD19-CAR T-cell therapy due to T-cell intrinsic and/or extrinsic mechanisms. Thus, there is a need to evaluate new CD19-CAR T-cell products in patients to improve efficacy. We developed a phase 1/2 clinical study to evaluate an institutional autologous CD19-CAR T-cell product in pediatric patients with relapsed/refractory B-ALL. Here we report the outcome of the phase 1 study participants (n = 12). Treatment was well tolerated, with a low incidence of both cytokine release syndrome (any grade, n = 6) and neurotoxicity (any grade, n = 3). Nine out of 12 patients (75%) achieved a minimal residual disease-negative CR in the bone marrow (BM). High disease burden (≥40% morphologic blasts) before CAR T-cell infusion correlated with increased side effects and lower response rate, but not with CD19-CAR T-cell expansion. After infusion, CD8+ CAR T cells had a proliferative advantage over CD4+ CAR T cells and at peak expansion, had an effector memory phenotype with evidence of antigen-driven differentiation. Patients that proceeded to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (AlloHCT) had sustained, durable responses. In summary, the initial evaluation of our institutional CD19-CAR T-cell product demonstrates safety and efficacy while highlighting the impact of pre-infusion disease burden on outcomes. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT03573700.
© 2022 by The American Society of Hematology. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: A. Sharma consults/consulted for Spotlight Therapeutics and Medexus Inc. B.Y. consults/consulted for ElevateBio. S.G. consults/consulted for TESSA Therapeutics, TIDAL, Catamaran, and Novartis. S.G. is a Data Safety and Monitoring Board (DSMB) member of Immatics. M.P.V. is a member of the Medical Advisory Board for the Rally Foundation. M.P.V., B.Y., C.Z., J.C.C., P.G.T., and S.G. have patents/patent applications in he fields of T-cell and/or gene therapy for cancer. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Mullard A. FDA approves fourth CAR-T cell therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021;20(3):166. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

