Artificial neural network-based estimation of COVID-19 case numbers and effective reproduction rate using wastewater-based epidemiology
- PMID: 35447417
- PMCID: PMC9006161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118451
Artificial neural network-based estimation of COVID-19 case numbers and effective reproduction rate using wastewater-based epidemiology
Abstract
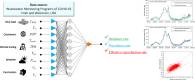
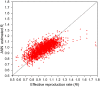
As a cost-effective and objective population-wide surveillance tool, wastewater-based epidemiology (WBE) has been widely implemented worldwide to monitor the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA concentration in wastewater. However, viral concentrations or loads in wastewater often correlate poorly with clinical case numbers. To date, there is no reliable method to back-estimate the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) case numbers from SARS-CoV-2 concentrations in wastewater. This greatly limits WBE in achieving its full potential in monitoring the unfolding pandemic. The exponentially growing SARS-CoV-2 WBE dataset, on the other hand, offers an opportunity to develop data-driven models for the estimation of COVID-19 case numbers (both incidence and prevalence) and transmission dynamics (effective reproduction rate). This study developed artificial neural network (ANN) models by innovatively expanding a conventional WBE dataset to include catchment, weather, clinical testing coverage and vaccination rate. The ANN models were trained and evaluated with a comprehensive state-wide wastewater monitoring dataset from Utah, USA during May 2020 to December 2021. In diverse sewer catchments, ANN models were found to accurately estimate the COVID-19 prevalence and incidence rates, with excellent precision for prevalence rates. Also, an ANN model was developed to estimate the effective reproduction number from both wastewater data and other pertinent factors affecting viral transmission and pandemic dynamics. The established ANN model was successfully validated for its transferability to other states or countries using the WBE dataset from Wisconsin, USA.
Keywords: Artificial neural network; COVID-19; Incidence; Prevalence; SARS-CoV-2; Wastewater-based epidemiology.
Copyright © 2022. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:
Guangming Jiang reports financial support was provided by Australian Research Council. Guangming Jiang reports financial support was provided by Australian Academy of Science. Guangming Jiang reports financial support was provided by Australian Government Department of Industry Science Energy and Resources.
Figures

References
-
- Abdeldayem O.M., Dabbish A.M., Habashy M.M., Mostafa M.K., Elhefnawy M., Amin L., Al-Sakkari E.G., Ragab A., Rene E.R. Viral outbreaks detection and surveillance using wastewater-based epidemiology, viral air sampling, and machine learning techniques: a comprehensive review and outlook. Sci. Total Environ. 2022;803 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acosta N., Bautista M.A., Hollman J., McCalder J., Beaudet A.B., Man L., Waddell B.J., Chen J., Li C., Kuzma D., Bhatnagar S., Leal J., Meddings J., Hu J., Cabaj J.L., Ruecker N.J., Naugler C., Pillai D.R., Achari G., Ryan M.C., Conly J.M., Frankowski K., Hubert C.R., Parkins M.D. A multicenter study investigating SARS-CoV-2 in tertiary-care hospital wastewater. viral burden correlates with increasing hospitalized cases as well as hospital-associated transmissions and outbreaks. Water Res. 2021;201 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Bertsch P.M., Angel N., Bibby K., Bivins A., Dierens L., Edson J., Ehret J., Gyawali P., Hamilton K., Hosegood I., Hugenholtz P., Jiang G., Kitajima M., Sichani H.T., Shi J., Shimko K.M., Simpson S.L., Smith W.J.M., Symonds E.M., Thomas DSC K.V., Verhagen R., Zaugg J., Mueller J.F. Detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in commercial passenger aircraft and cruise ship wastewater: a surveillance tool for assessing the presence of COVID-19 infected travelers. J. Travel Med. 2020 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ahmed W., Bertsch P.M., Bibby K., Haramoto E., Hewitt J., Huygens F., Gyawali P., Korajkic A., Riddell S., Sherchan S.P., Simpson S.L., Sirikanchana K., Symonds E.M., Verhagen R., Vasan S.S., Kitajima M., Bivins A. Decay of SARS-CoV-2 and surrogate murine hepatitis virus RNA in untreated wastewater to inform application in wastewater-based epidemiology. Environ. Res. 2020;191 -110092. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

