Current advances in the treatment of systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 35447517
- PMCID: PMC9466985
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coph.2022.102211
Current advances in the treatment of systemic sclerosis
Abstract
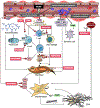
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a rare, systemic autoimmune disease of unknown etiology. Among the systemic rheumatic diseases, SSc carries the highest mortality, in part due to the historical lack of disease modifying therapies. Recently, landmark randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have been conducted that have illustrated the heterogeneous nature of SSc and furthered our understanding of the key inflammatory and fibrotic pathways involved in SSc pathogenesis. Although SSc affects various organ systems, RCTs have focused on investigating treatments for diffuse cutaneous sclerosis (dcSSc) and interstitial lung disease (ILD). While recent RCTs for dcSSc have failed to demonstrate a treatment benefit, the outcomes of two RCTs led to the approval of two novel therapies for SSc-ILD: nintedanib and tocilizumab. This review summarizes the salient outcome data from recent SSc trials within a practical clinical framework and points out gaps in knowledge that may help inform the design of future SSc studies.
Keywords: Cutaneous sclerosis; Interstitial lung disease; Nintedanib; Systemic sclerosis; Therapeutics; Tocilizumab.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest None of the authors received any financial support or other benefits from commercial sources for the work reported in this manuscript, nor do any of the authors have any financial interests, which could create a potential conflict of interest or appearance thereof. ERV has received consulting fees from Boehringer Ingelheim and grant support for systemic sclerosis research and clinical trials from Kadmon, Horizon, Forbius, and Boehringer Ingelheim.
Figures

References
-
- Chung L, Domsic RT, Lingala B, Alkassab F, Bolster M, Csuka ME, Derk C, Fischer A, Frech T, Furst DE, et al. Survival and predictors of mortality in systemic sclerosis-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension: outcomes from the pulmonary hypertension assessment and recognition of outcomes in scleroderma registry. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(3):489–95. doi: 10.1002/acr.22121. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

