Predicting Academic Performance: Analysis of Students' Mental Health Condition from Social Media Interactions
- PMID: 35447659
- PMCID: PMC9027872
- DOI: 10.3390/bs12040087
Predicting Academic Performance: Analysis of Students' Mental Health Condition from Social Media Interactions
Abstract
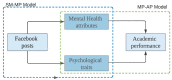
Social media have become an indispensable part of peoples' daily lives. Research suggests that interactions on social media partly exhibit individuals' personality, sentiment, and behavior. In this study, we examine the association between students' mental health and psychological attributes derived from social media interactions and academic performance. We build a classification model where students' psychological attributes and mental health issues will be predicted from their social media interactions. Then, students' academic performance will be identified from their predicted psychological attributes and mental health issues in the previous level. Firstly, we select samples by using judgmental sampling technique and collect the textual content from students' Facebook news feeds. Then, we derive feature vectors using MPNet (Masked and Permuted Pre-training for Language Understanding), which is one of the latest pre-trained sentence transformer models. Secondly, we find two different levels of correlations: (i) users' social media usage and their psychological attributes and mental health status and (ii) users' psychological attributes and mental health status and their academic performance. Thirdly, we build a two-level hybrid model to predict academic performance (i.e., Grade Point Average (GPA)) from students' Facebook posts: (1) from Facebook posts to mental health and psychological attributes using a regression model (SM-MP model) and (2) from psychological and mental attributes to the academic performance using a classifier model (MP-AP model). Later, we conduct an evaluation study by using real-life samples to validate the performance of the model and compare the performance with Baseline Models (i.e., Linguistic Inquiry and Word Count (LIWC) and Empath). Our model shows a strong performance with a microaverage f-score of 0.94 and an AUC-ROC score of 0.95. Finally, we build an ensemble model by combining both the psychological attributes and the mental health models and find that our combined model outperforms the independent models.
Keywords: BiLSTM; Facebook; MPNet; classification; ensemble; psychological attributes and mental health; regression; word embedding.
Conflict of interest statement
The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
-
- Komarraju M., Karau S.J., Schmeck R.R., Avdic A. The Big Five personality traits, learning styles, and academic achievement. Personal. Individ. Differ. 2011;51:472–477. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2011.04.019. - DOI
-
- Boon L.K., Fern Y.S., Sze C.C. Factors affecting individual job performance; Proceedings of the International Conference on Management Finance and Economics; Sarawak, Malaysia. 15–16 October 2012.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

