Heart Rate Variability Analysis for Seizure Detection in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
- PMID: 35447725
- PMCID: PMC9031489
- DOI: 10.3390/bioengineering9040165
Heart Rate Variability Analysis for Seizure Detection in Neonatal Intensive Care Units
Abstract
In Neonatal Intensive Care Units (NICUs), the early detection of neonatal seizures is of utmost importance for a timely clinical intervention. Over the years, several neonatal seizure detection systems were proposed to detect neonatal seizures automatically and speed up seizure diagnosis, most based on the EEG signal analysis. Recently, research has focused on other possible seizure markers, such as electrocardiography (ECG). This work proposes an ECG-based NSD system to investigate the usefulness of heart rate variability (HRV) analysis to detect neonatal seizures in the NICUs. HRV analysis is performed considering time-domain, frequency-domain, entropy and multiscale entropy features. The performance is evaluated on a dataset of ECG signals from 51 full-term babies, 29 seizure-free. The proposed system gives results comparable to those reported in the literature: Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve = 62%, Sensitivity = 47%, Specificity = 67%. Moreover, the system's performance is evaluated in a real clinical environment, inevitably affected by several artefacts. To the best of our knowledge, our study proposes for the first time a multi-feature ECG-based NSD system that also offers a comparative analysis between babies suffering from seizures and seizure-free ones.
Keywords: ECG; HRV; NICU; multiscale entropy; neonatal seizures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



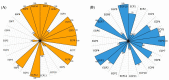
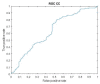
Similar articles
-
Multiscale Entropy Analysis of Heart Rate Variability in Neonatal Patients with and without Seizures.Bioengineering (Basel). 2021 Sep 9;8(9):122. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8090122. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34562944 Free PMC article.
-
A Generalized Linear Model for an ECG-based Neonatal Seizure Detector.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021 Nov;2021:471-474. doi: 10.1109/EMBC46164.2021.9630841. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2021. PMID: 34891335
-
Combination of EEG and ECG for improved automatic neonatal seizure detection.Clin Neurophysiol. 2007 Jun;118(6):1348-59. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2007.02.015. Epub 2007 Mar 29. Clin Neurophysiol. 2007. PMID: 17398146
-
Monitoring neonatal seizures.Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013 Aug;18(4):202-8. doi: 10.1016/j.siny.2013.04.004. Epub 2013 May 24. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2013. PMID: 23707519 Review.
-
The role of electroencephalogram in neonatal seizure detection.Expert Rev Neurother. 2018 Feb;18(2):95-100. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2018.1413352. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Expert Rev Neurother. 2018. PMID: 29199490 Review.
Cited by
-
Heart Rate Variability as a Tool for Seizure Prediction: A Scoping Review.J Clin Med. 2024 Jan 27;13(3):747. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030747. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shellhaas R.A., Chang T., Tsuchida T., Scher M.S., Riviello J.J., Abend N.S., Nguyen S., Wusthoff C.J., Clancy R.R. The American Clinical Neurophysiology Society’s Guideline on Continuous Electroencephalography Monitoring in Neonates. J. Clin. Neurophysiol. Off. Publ. Am. Electroencephalogr. Soc. 2011;28:611–617. doi: 10.1097/WNP.0b013e31823e96d7. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

