Transcriptional Regulation of Reproductive Diapause in the Convergent Lady Beetle, Hippodamia convergens
- PMID: 35447785
- PMCID: PMC9026804
- DOI: 10.3390/insects13040343
Transcriptional Regulation of Reproductive Diapause in the Convergent Lady Beetle, Hippodamia convergens
Abstract
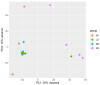
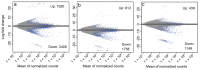
Diapause is an alternate development program that synchronizes an insect's life cycle with seasonally abundant resources and ensures survival in unfavorable conditions. The physiological basis of diapause has been well characterized, but the molecular mechanisms regulating it are still being elucidated. Here, we present a de novo transcriptome and quantify transcript expression during diapause in the convergent lady beetle Hippodamia convergens. H. convergens is used as an augmentative biocontrol agent, and adult females undergo reproductive diapause that is regulated by photoperiod. We sampled females at three stages (early, mid, and late diapause) and compared transcript expression to non-diapausing individuals. Based on principle component analysis, the transcriptomes of diapausing beetles were distinct from non-diapausing beetles, and the three diapausing points tended to cluster together. However, there were still classes of transcripts that differed in expression across distinct phases of diapause. In general, transcripts involved in muscle function and flight were upregulated during diapause, likely to support dispersal flights that occur during diapause, while transcripts involved in ovarian development were downregulated. This information could be used to improve biological control by manipulating diapause. Additionally, our data contribute to a growing understanding of the genetic regulation of diapause across diverse insects.
Keywords: Coleoptera; RNA-Seq; biological control; reproductive diapause; transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Denlinger D.L., Joplin K.H., Flannagan R.D., Tammariello S.P., Zhang M.-L., Yocum G.D., Lee K.-Y. Diapause-Specific Gene Expression. In: Suzuki A., Kataoka H., Matsumoto S., editors. Molecular Mechanisms of Insect Metamorphosis and Diapause. Industrial Publishing; Tokyo, Japan: 1995. pp. 289–297.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

