Hypertension and Arrhythmias: A Clinical Overview of the Pathophysiology-Driven Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Hypertensive Patients
- PMID: 35448086
- PMCID: PMC9025699
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9040110
Hypertension and Arrhythmias: A Clinical Overview of the Pathophysiology-Driven Management of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
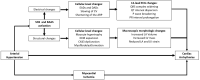
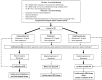
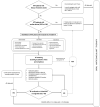
Because of demographic aging, the prevalence of arterial hypertension (HTN) and cardiac arrhythmias, namely atrial fibrillation (AF), is progressively increasing. Not only are these clinical entities strongly connected, but, acting with a synergistic effect, their association may cause a worse clinical outcome in patients already at risk of ischemic and/or haemorrhagic stroke and, consequently, disability and death. Despite the well-known association between HTN and AF, several pathogenetic mechanisms underlying the higher risk of AF in hypertensive patients are still incompletely known. Although several trials reported the overall clinical benefit of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors in reducing incident AF in HTN, the role of this class of drugs is greatly reduced when AF diagnosis is already established, thus hinting at the urgent need for primary prevention measures to reduce AF occurrence in these patients. Through a thorough review of the available literature in the field, we investigated the basic mechanisms through which HTN is believed to promote AF, summarising the evidence supporting a pathophysiology-driven approach to prevent this arrhythmia in hypertensive patients, including those suffering from primary aldosteronism, a non-negligible and under-recognised cause of secondary HTN. Finally, in the hazy scenario of AF screening in hypertensive patients, we reviewed which patients should be screened, by which modality, and who should be offered oral anticoagulation for stroke prevention.
Keywords: anticoagulants; antihypertensive agents; artificial pacemakers; atrial fibrillation; hypertension; primary hyperaldosteronism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Williams B., Mancia G., Spiering W., Agabiti Rosei E., Azizi M., Burnier M., Clement D.L., Coca A., de Simone G., Dominiczak A., et al. ESC/ESH Guidelines for the Management of Arterial Hypertension, The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension, The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology and the European Society of Hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2018;36:1953–2041. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000001940. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Chow C.K., Teo K.K., Rangarajan S., Islam S., Gupta R., Avezum A., Bahonar A., Chifamba J., Dagenais G., Diaz R., et al. PURE Study Investigators. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension in rural and urban communities in high-, middle-, and low-income countries. JAMA. 2013;310:959–968. doi: 10.1001/jama.2013.184182. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lip G.Y.H., Coca A., Kahan T., Boriani G., Manolis A.S., Olsen M.H., Oto A., Potpara T.S., Steffel J., Marín F., et al. Hypertension and cardiac arrhythmias, A consensus document from the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) and ESC Council on Hypertension, endorsed by the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS), Asia-Pacific Heart Rhythm Society (APHRS) and Sociedad Latinoamericana de Estimulacion Cardiaca y Electrofisiologia (SOLEACE) Europace. 2017;19:891–911. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

