Whole Genome Sequencing in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
- PMID: 35448093
- PMCID: PMC9028226
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd9040117
Whole Genome Sequencing in Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
Abstract
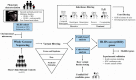
Hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) is a genetically complex disorder. Whole genome sequencing enables comprehensive scrutiny of single nucleotide variants and small insertions/deletions, within both coding and regulatory regions of the genome, revolutionizing susceptibility-gene discovery research. Because millions of rare variants comprise an individual genome, identification of alleles linked to HLHS necessitates filtering algorithms based on various parameters, such as inheritance, enrichment, omics data, known genotype-phenotype associations, and predictive or experimental modeling. In this brief review, we highlight family and cohort-based strategies used to analyze whole genome sequencing datasets and identify HLHS candidate genes. Key findings include compound and digenic heterozygosity among several prioritized genes and genetic associations between HLHS and bicuspid aortic valve or cardiomyopathy. Together with findings of independent genomic investigations, MYH6 has emerged as a compelling disease gene for HLHS and other left-sided congenital heart diseases.
Keywords: MYH6; congenital heart disease; genetics; hypoplastic left heart syndrome; whole genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Olson J.E., Ryu E., Johnson K.J., Koenig B.A., Maschke K.J., Morrisette J.A., Liebow M., Takahashi P.Y., Fredericksen Z.S., Sharma R.G., et al. The Mayo Clinic Biobank: A building block for individualized medicine. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013;88:952–962. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2013.06.006. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McBride K.L., Pignatelli R., Lewin M., Ho T., Fernbach S., Menesses A., Lam W., Leal S.M., Kaplan N., Schliekelman P., et al. Inheritance analysis of congenital left ventricular outflow tract obstruction malformations: Segregation, multiplex relative risk, and heritability. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A. 2005;134A:180–186. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.30602. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

