Comprehensive Treatment of Hematological Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection Including Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies: A Single-Center Experience Case Series
- PMID: 35448162
- PMCID: PMC9032833
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29040188
Comprehensive Treatment of Hematological Patients with SARS-CoV-2 Infection Including Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Monoclonal Antibodies: A Single-Center Experience Case Series
Abstract
Patients with hematologic malignancies are at high risk of exacerbated condition and higher mortality from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Bamlanivimab, casirivimab/imdevimab combination, and sotrovimab are monoclonal antibodies (mABs) that can reduce the risk of COVID-19-related hospitalization. Clinical effectiveness of bamlanivimab and casirivimab/imdevimab combination has been shown for the Delta variant (B.1.617.2), but the effectiveness of the latter treatment against the Omicron variant (B.1.1.529) has been suggested to be reduced. However, the tolerability and clinical usage of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)-specific mABs in patients with hematologic malignancies are less specified. We present a retrospective case series analysis of all SARS-CoV-2-infected patients with hematologic malignancies who received SARS-CoV-2-specific mABs at our facility between February and mid-December 2021. A total of 13 COVID-19 patients (pts) with at least one malignant hematologic diagnosis received SARS-CoV-2-specific mABs at our facility, with 3 pts receiving bamlanivimab and 10 pts receiving casirivimab/imdevimab combination. We observed SARS-CoV-2 clearance in five cases. Furthermore, we observed a reduction in the necessity for oxygen supplementation in five cases where the application was administered off-label. To the best of our knowledge, we present the largest collection of anecdotal cases of SARS-CoV-2-specific monoclonal antibody use in patients with hematological malignancies. Potential benefit of mABs may be reduced duration and/or clearance of persistent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; antibody therapy; bamlanivimab; cancer; casirivimab; hematologic malignancies; imdevimab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
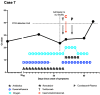

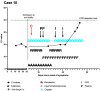

References
-
- Tomazini B.M., Maia I.S., Cavalcanti A.B., Berwanger O., Rosa R.G., Veiga V.C., Avezum A., Lopes R.D., Bueno F.R., Silva M., et al. Effect of Dexamethasone on Days Alive and Ventilator-Free in Patients with Moderate or Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and COVID-19: The CoDEX Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama. 2020;324:1307–1316. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Munch M.W., Myatra S.N., Vijayaraghavan B.K.T., Saseedharan S., Benfield T., Wahlin R.R., Rasmussen B.S., Andreasen A.S., Poulsen L.M., Cioccari L., et al. Effect of 12 mg vs 6 mg of Dexamethasone on the Number of Days Alive without Life Support in Adults with COVID-19 and Severe Hypoxemia: The COVID STEROID 2 Randomized Trial. Jama. 2021;326:1807–1817. doi: 10.1001/jama.2021.18295. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

