Motivation to Consent and Adhere to the FORT Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 35448206
- PMCID: PMC9025660
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol29040232
Motivation to Consent and Adhere to the FORT Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
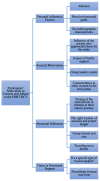
The aim of this qualitative study was to identify the motivational factors that influence cancer survivors to participate and adhere to the fear of cancer recurrence (FCR) FORT randomized controlled trial (RCT). Fifteen women diagnosed with breast and gynecological cancer who took part in the FORT RCT were interviewed about their experience to consent and adhere to the trial. The transcribed interviews were content analyzed within a relational autonomy framework. The analysis revealed that the participants' motivation to consent and adhere to the FORT RCT was structured around thirteen subthemes grouped into four overarching themes: (1) Personal Influential Factors; (2) Societal Motivations; (3) Structural Influences; and (4) Gains in Emotional Support. The unique structures of the trial such as the group format, the friendships formed with other participants in their group and with the group leaders, and the right timing of the trial within their cancer survivorship trajectory all contributed to their motivation to consent and adhere to the FORT RCT. While their initial motivation to participate was mostly altruistic, it was their personal gains obtained over the course of the trial that contributed to their adherence. Potential gains in emotional and social support from psycho-oncology trials should be capitalized when approaching future participants as a mean to improve on motivations to consent and adhere.
Keywords: breast and gynecological cancer; clinical trial; cognitive-existential approach; fear of cancer recurrence; group intervention; interpretive description.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protocol of a randomized controlled trial of the fear of recurrence therapy (FORT) intervention for women with breast or gynecological cancer.BMC Cancer. 2016 Apr 25;16:291. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2326-x. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27112319 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Fear of cancer recurrence therapy (FORT): A randomized controlled trial.Health Psychol. 2023 Mar;42(3):182-194. doi: 10.1037/hea0001253. Health Psychol. 2023. PMID: 36862474 Clinical Trial.
-
Study protocol of the BLANKET trial: a cluster randomised controlled trial on the (cost-) effectiveness of a primary care intervention for fear of cancer recurrence in cancer survivors.BMJ Open. 2019 Dec 2;9(12):e032616. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2019-032616. BMJ Open. 2019. PMID: 31796488 Free PMC article.
-
Motivational strategies to improve adherence to physical activity in breast cancer survivors: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Maturitas. 2021 Oct;152:32-47. doi: 10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.06.008. Epub 2021 Jun 24. Maturitas. 2021. PMID: 34674806
-
[Factors Influencing Patient Decisions Regarding Cancer Clinical Trial Participation: A Systematic Review].Hu Li Za Zhi. 2022 Feb;69(1):83-99. doi: 10.6224/JN.202202_69(1).11. Hu Li Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 35080001 Chinese.
References
-
- Lebel S., Ozakinci G., Humphris G., Mutsaers B., Thewes B., Prins J., Dinkel A., Butow P., Univ on behalf of the University of Ottawa Fear of Cancer Recurrence Colloquium attendees From normal response to clinical problem: Definition and clinical features of fear of cancer recurrence. Support. Care Cancer. 2016;24:3265–3268. doi: 10.1007/s00520-016-3272-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Canadian Partnership against Cancer . In: Living with Cancer: A Report on the Patient Experience. Canadian Partnership against Cancer, editor. Canadian Partnership against Cancer; Toronto, ON, Canada: 2018. p. 50.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical