YOLOv4-Based CNN Model versus Nested Contours Algorithm in the Suspicious Lesion Detection on the Mammography Image: A Direct Comparison in the Real Clinical Settings
- PMID: 35448216
- PMCID: PMC9031201
- DOI: 10.3390/jimaging8040088
YOLOv4-Based CNN Model versus Nested Contours Algorithm in the Suspicious Lesion Detection on the Mammography Image: A Direct Comparison in the Real Clinical Settings
Abstract
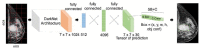
Background: We directly compared the mammography image processing results obtained with the help of the YOLOv4 convolutional neural network (CNN) model versus those obtained with the help of the NCA-based nested contours algorithm model.
Method: We used 1080 images to train the YOLOv4, plus 100 images with proven breast cancer (BC) and 100 images with proven absence of BC to test both models.
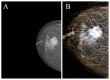
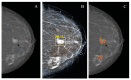
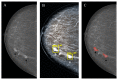
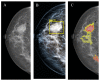
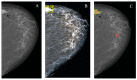
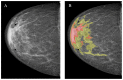
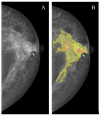
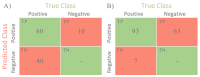
Results: the rates of true-positive, false-positive and false-negative outcomes were 60, 10 and 40, respectively, for YOLOv4, and 93, 63 and 7, respectively, for NCA. The sensitivities for the YOLOv4 and the NCA were comparable to each other for star-like lesions, masses with unclear borders, round- or oval-shaped masses with clear borders and partly visualized masses. On the contrary, the NCA was superior to the YOLOv4 in the case of asymmetric density and of changes invisible on the dense parenchyma background. Radiologists changed their earlier decisions in six cases per 100 for NCA. YOLOv4 outputs did not influence the radiologists' decisions.
Conclusions: in our set, NCA clinically significantly surpasses YOLOv4.
Keywords: YOLOv4; breast cancer; convolutional neural network; mammography; nested contours algorithm.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Detection of Pine Wilt Nematode from Drone Images Using UAV.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Jun 22;22(13):4704. doi: 10.3390/s22134704. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808205 Free PMC article.
-
Nature-Inspired Search Method and Custom Waste Object Detection and Classification Model for Smart Waste Bin.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Aug 18;22(16):6176. doi: 10.3390/s22166176. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015936 Free PMC article.
-
A preliminary study on computerized lesion localization in MR mammography using 3D nMITR maps, multilayer cellular neural networks, and fuzzy c-partitioning.Med Phys. 2008 Jan;35(1):195-205. doi: 10.1118/1.2805477. Med Phys. 2008. PMID: 18293575
-
Improved YOLOv4-tiny based on attention mechanism for skin detection.PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023 Mar 10;9:e1288. doi: 10.7717/peerj-cs.1288. eCollection 2023. PeerJ Comput Sci. 2023. PMID: 37346516 Free PMC article.
-
Convolutional neural networks for breast cancer detection in mammography: A survey.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Apr;131:104248. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104248. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33631497 Review.
Cited by
-
Presegmenter Cascaded Framework for Mammogram Mass Segmentation.Int J Biomed Imaging. 2024 Aug 9;2024:9422083. doi: 10.1155/2024/9422083. eCollection 2024. Int J Biomed Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39155940 Free PMC article.
-
Siam Deep Feature KCF Method and Experimental Study for Pedestrian Tracking.Sensors (Basel). 2023 Jan 2;23(1):482. doi: 10.3390/s23010482. Sensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36617099 Free PMC article.
-
Elimination of Defects in Mammograms Caused by a Malfunction of the Device Matrix.J Imaging. 2022 May 2;8(5):128. doi: 10.3390/jimaging8050128. J Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35621892 Free PMC article.
-
A Survey of Convolutional Neural Network in Breast Cancer.Comput Model Eng Sci. 2023 Mar 9;136(3):2127-2172. doi: 10.32604/cmes.2023.025484. Comput Model Eng Sci. 2023. PMID: 37152661 Free PMC article.
-
TRUST: A Novel Framework for Vehicle Trajectory Recovery from Urban-Scale Videos.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 16;22(24):9948. doi: 10.3390/s22249948. Sensors (Basel). 2022. Retraction in: Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jun 06;24(11):3672. doi: 10.3390/s24113672. PMID: 36560317 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

