MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/Cellulose Acetate Mixed-Matrix Membrane Enhances Fouling Resistance and Rejection in the Crossflow Filtration Process
- PMID: 35448377
- PMCID: PMC9027356
- DOI: 10.3390/membranes12040406
MXene (Ti3C2Tx)/Cellulose Acetate Mixed-Matrix Membrane Enhances Fouling Resistance and Rejection in the Crossflow Filtration Process
Abstract
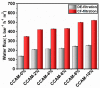
Obstacles in the membrane-based separation field are mainly related to membrane fouling. This study involved the synthesis and utilization of covalently crosslinked MXene/cellulose acetate mixed matrix membranes with MXene at different concentrations (CCAM-0% to CCAM-12%) for water purification applications. The membranes' water flux, dye, and protein rejection performances were compared using dead-end (DE) and crossflow (CF) filtration. The fabricated membranes, especially CCAM-10%, exhibited high hydrophilicity, good surface roughness, significantly high water flux, high water uptake, and high porosity. A significantly higher flux was observed in CF filtration relative to DE filtration. Moreover, in CF filtration, the CCAM-10% membrane exhibited 96.60% and 99.49% rejection of methyl green (MG) and bovine serum albumin (BSA), respectively, while maintaining a flux recovery ratio of 67.30% and an irreversible fouling ratio at (Rir) of 32.70, indicating good antifouling performance. Hence, this study suggests that covalent modification of cellulose acetate membranes with MXene significantly improves the performance and fouling resistance of membranes for water filtration in CF mode relative to DE mode.
Keywords: MXene; antifouling; crossflow; membrane filtration.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Al-Najar B., Peters C.D., Albuflasa H., Hankins N.P. Pressure and osmotically driven membrane processes: A review of the benefits and production of nano-enhanced membranes for desalination. Desalination. 2020;479:114323. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2020.114323. - DOI
-
- Bodzek M., Konieczny K., Kwiecińska A. Application of membrane processes in drinking water treatment–state of art. Desalination Water Treat.-DESALIN WATER TREAT. 2011;35:164–184. doi: 10.5004/dwt.2011.2435. - DOI
-
- Modi A., Bellare J. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-67/carboxylated graphene oxide nanosheets incorporated polyethersulfone hollow fiber membranes for removal of toxic heavy metals from contaminated water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020;249:117160. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.117160. - DOI
-
- Karimnezhad H., Navarchian A.H., Tavakoli Gheinani T., Zinadini S. Incorporation of iron oxyhydroxide nanoparticles in polyacrylonitrile nanofiltration membrane for improving water permeability and antifouling property. React. Funct. Polym. 2019;135:77–93. doi: 10.1016/j.reactfunctpolym.2018.12.016. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

