Comparison Approach for Identifying Missed Invasive Fungal Infections in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Autopsy Specimens
- PMID: 35448568
- PMCID: PMC9030445
- DOI: 10.3390/jof8040337
Comparison Approach for Identifying Missed Invasive Fungal Infections in Formalin-Fixed, Paraffin-Embedded Autopsy Specimens
Abstract
Invasive fungal infection (IFI) has a high mortality rate in patients who undergo hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and it is often confirmed by postmortem dissection. When IFI is initially confirmed after an autopsy, the tissue culture and frozen section are challenging to secure, and in many cases, formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples represent the only modality for identifying fungi. Histopathological diagnosis is a useful method in combination with molecular biological methods that can achieve more precise identification with reproducibility. Meanwhile, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using fungal-specific primers helps identify fungi from FFPE tissues. Autopsy FFPE specimens have a disadvantage regarding the quality of DNA extracted compared with that of specimens obtained via biopsy or surgery. In the case of mucormycosis diagnosed postmortem histologically, we examined currently available molecular biological methods such as PCR, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and in situ hybridization (ISH) to identify fungi. It is reasonable that PCR with some modification is valuable for identifying fungi in autopsy FFPE specimens. However, PCR does not always correctly identify fungi in autopsy FFPE tissues, and other approaches such as ISH or IHC are worth considering for clarifying the broad classification (such as the genus- or species-level classification).
Keywords: Cunninghamella; autopsy; formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE); immunohistochemistry (IHC); in situ hybridization (ISH); invasive fungal infection (IFI); mucormycosis; polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
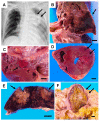
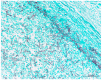
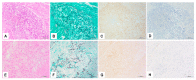
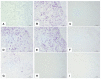
References
-
- Lockhart S.R., Bialek R., Kibbler C.C., Cuenca-Estrella M., Jensen H.E., Kontoyiannis D.P. Molecular Techniques for Genus and Species Determination of Fungi from Fresh and Paraffin-Embedded Formalin-Fixed Tissue in the Revised EORTC/MSGERC Definitions of Invasive Fungal Infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021;72:S109–S113. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1836. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

