Predicting RNA splicing from DNA sequence using Pangolin
- PMID: 35449021
- PMCID: PMC9022248
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-022-02664-4
Predicting RNA splicing from DNA sequence using Pangolin
Abstract
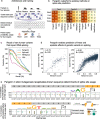
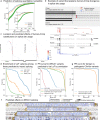
Recent progress in deep learning has greatly improved the prediction of RNA splicing from DNA sequence. Here, we present Pangolin, a deep learning model to predict splice site strength in multiple tissues. Pangolin outperforms state-of-the-art methods for predicting RNA splicing on a variety of prediction tasks. Pangolin improves prediction of the impact of genetic variants on RNA splicing, including common, rare, and lineage-specific genetic variation. In addition, Pangolin identifies loss-of-function mutations with high accuracy and recall, particularly for mutations that are not missense or nonsense, demonstrating remarkable potential for identifying pathogenic variants.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Baeza-Centurion P, Miñana B, Schmiedel JM, Valcárcel J, Lehner B. Combinatorial Genetics Reveals a Scaling Law for the Effects of Mutations on Splicing. Cell. 2019;176(3):549–63. - PubMed
-
- Blencowe BJ. Exonic splicing enhancers: mechanism of action, diversity and role in human genetic diseases. Trends Biochem Sci. 2000;25(3):106–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

