Ultrasound localization of central vein catheter tip by contrast-enhanced transthoracic ultrasonography: a comparison study with trans-esophageal echocardiography
- PMID: 35449059
- PMCID: PMC9027702
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-022-03985-3
Ultrasound localization of central vein catheter tip by contrast-enhanced transthoracic ultrasonography: a comparison study with trans-esophageal echocardiography
Abstract
Background: To assess the usefulness of pre-operative contrast-enhanced transthoracic echocardiography (CE-TTE) and post-operative chest-x-ray (CXR) for evaluating central venous catheter (CVC) tip placements, with trans-esophageal echocardiography (TEE) as gold standard.
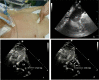
Methods: A prospective single-center, observational study was performed in 111 patients requiring CVC positioning into the internal jugular vein for elective cardiac surgery. At the end of CVC insertion by landmark technique, a contrast-enhanced TTE was performed by both the apical four-chambers and epigastric bicaval acoustic view to assess catheter tip position; then, a TEE was performed and considered as a reference technique. A postoperative CXR was obtained for all patients.
Results: As per TEE, 74 (67%) catheter tips were correctly placed and 37 (33%) misplaced. Considering intravascular and intracardiac misplacements together, they were detected in 8 patients by CE-TTE via apical four-chamber view, 36 patients by CE-TTE via epigastric bicaval acoustic view, and 12 patients by CXR. For the detection of catheter tip misplacement, CE-TTE via epigastric bicaval acoustic view was the most accurate method providing 97% sensitivity, 90% specificity, and 92% diagnostic accuracy if compared with either CE-TTE via apical four-chamber view or CXR. Concordance with TEE was 79% (p < 0.001) for CE-TTE via epigastric bicaval acoustic view.
Conclusions: The concordance between CE-TTE via epigastric bicaval acoustic view and TEE suggests the use of the former as a standard technique to ensure the correct positioning of catheter tip after central venous cannulation to optimize the use of hospital resources and minimize radiation exposure.
Keywords: Bubble test; CVC misplacements; Cardiac surgery patients; Central venous catheterization; Chest radiography; Internal jugular vein cannulation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests with the subject of the article.
Figures



References
-
- Kolikof J, Peterson K, Baker AM. Central Venous Catheter. StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2021 [cited 2021 Sep 14]. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557798/ - PubMed
-
- Hoch JR. Management of the complications of long-term venous access. Semin Vasc Surg. 1997;10:135–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

