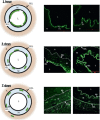
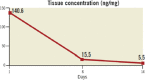
Major adverse limb events in patients with femoro-popliteal and below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease treated with either sirolimus-coated balloon or standard uncoated balloon angioplasty: a structured protocol summary of the "SirPAD" randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 35449070
- PMCID: PMC9027348
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-022-06242-8
Major adverse limb events in patients with femoro-popliteal and below-the-knee peripheral arterial disease treated with either sirolimus-coated balloon or standard uncoated balloon angioplasty: a structured protocol summary of the "SirPAD" randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Peripheral arterial disease is a progressive atherosclerotic disease with symptoms ranging from an intermittent claudication to acute critical limb ischemia and amputations. Drug-coated balloons and stents were developed to prevent neo-intimal proliferation and restenosis after percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Randomized controlled trials showed that drug-coated, notably paclitaxel-coated, devices reduce restenosis, late lumen loss, and the need for target lesion re-vascularization compared with uncoated ones. However, the size of these trials was too small to prove superiority for "hard" clinical outcomes. Moreover, available studies were characterized by too restrictive eligibility criteria. Finally, it remains unclear whether paclitaxel-coated balloons may impair long-term survival. Alternative drug-coated balloons, the so-called limus-based analogs, have been approved for clinical use in patients with peripheral arterial disease. By encapsulating sirolimus in phospholipid drug nanocarriers, they optimize adhesion properties of sirolimus and provide better bioavailability.
Methods: In this investigator-initiated all-comer open-label phase III randomized controlled trial, we will evaluate whether sirolimus-coated balloon angioplasty is non-inferior and eventually superior, according to a predefined hierarchical analysis, to uncoated balloon angioplasty in adults with infra-inguinal peripheral arterial disease requiring endovascular angioplasty. Key exclusion criteria are pregnancy or breastfeeding, known intolerance or allergy to sirolimus, and participation in a clinical trial during the previous 3 months. The primary efficacy outcome is the composite of two clinically relevant non-subjective "hard" outcomes: unplanned major amputation of the target limb and endovascular or surgical target lesion re-vascularization for critical limb ischemia occurring within 1 year of randomization. The primary safety outcome includes death from all causes.
Discussion: By focusing on clinically relevant outcomes, this study will provide useful information on the efficacy and safety of sirolimus-coated balloon catheters for infra-inguinal peripheral arterial disease in a representative ("all-comer") population of unselected patients. As regulatory agencies had raised safety concerns in patients exposed to paclitaxel-coated devices (versus uncoated ones), collect mortality data up to 5 years after randomization will be collected.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04238546.
Keywords: Atherosclerotic disease; Common iliac artery; Covered stent; Critical limb ischemia; Endovascular; Intermittent claudication; Peripheral arterial occlusive disease; Sirolimus; Stenting.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Song P, Rudan D, Zhu Y, Fowkes FJI, Rahimi K, Fowkes FGR, Rudan I. Global, regional, and national prevalence and risk factors for peripheral artery disease in 2015: an updated systematic review and analysis. Lancet Glob Health. 2019;7(8):e1020–e1030. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(19)30255-4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- European Stroke O, Tendera M, Aboyans V, et al. ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of peripheral artery diseases: document covering atherosclerotic disease of extracranial carotid and vertebral, mesenteric, renal, upper and lower extremity arteries: the Task Force on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Artery Diseases of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Eur Heart J. 2011;32(22):2851–2906. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr211. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dake MD, Ansel GM, Jaff MR, Ohki T, Saxon RR, Smouse HB, Zeller T, Roubin GS, Burket MW, Khatib Y, Snyder SA, Ragheb AO, White JK, Machan LS, Zilver PTX Investigators Paclitaxel-eluting stents show superiority to balloon angioplasty and bare metal stents in femoropopliteal disease: twelve-month Zilver PTX randomized study results. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;4(5):495–504. doi: 10.1161/CIRCINTERVENTIONS.111.962324. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Rosenfield K, Jaff MR, White CJ, Rocha-Singh K, Mena-Hurtado C, Metzger DC, Brodmann M, Pilger E, Zeller T, Krishnan P, Gammon R, Müller-Hülsbeck S, Nehler MR, Benenati JF, Scheinert D. Trial of a paclitaxel-coated balloon for femoropopliteal artery disease. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(2):145–153. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1406235. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scheinert D, Duda S, Zeller T, Krankenberg H, Ricke J, Bosiers M, Tepe G, Naisbitt S, Rosenfield K. The LEVANT I (Lutonix paclitaxel-coated balloon for the prevention of femoropopliteal restenosis) trial for femoropopliteal revascularization: first-in-human randomized trial of low-dose drug-coated balloon versus uncoated balloon angioplasty. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2014;7(1):10–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2013.05.022. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials