KMT2C deficiency promotes small cell lung cancer metastasis through DNMT3A-mediated epigenetic reprogramming
- PMID: 35449309
- PMCID: PMC9969417
- DOI: 10.1038/s43018-022-00361-6
KMT2C deficiency promotes small cell lung cancer metastasis through DNMT3A-mediated epigenetic reprogramming
Abstract
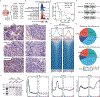
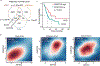
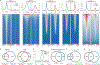
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is notorious for its early and frequent metastases, which contribute to it as a recalcitrant malignancy. To understand the molecular mechanisms underlying SCLC metastasis, we generated SCLC mouse models with orthotopically transplanted genome-edited lung organoids and performed multiomics analyses. We found that a deficiency of KMT2C, a histone H3 lysine 4 methyltransferase frequently mutated in extensive-stage SCLC, promoted multiple-organ metastases in mice. Metastatic and KMT2C-deficient SCLC displayed both histone and DNA hypomethylation. Mechanistically, KMT2C directly regulated the expression of DNMT3A, a de novo DNA methyltransferase, through histone methylation. Forced DNMT3A expression restrained metastasis of KMT2C-deficient SCLC through repressing metastasis-promoting MEIS/HOX genes. Further, S-(5'-adenosyl)-L-methionine, the common cofactor of histone and DNA methyltransferases, inhibited SCLC metastasis. Thus, our study revealed a concerted epigenetic reprogramming of KMT2C- and DNMT3A-mediated histone and DNA hypomethylation underlying SCLC metastasis, which suggested a potential epigenetic therapeutic vulnerability.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





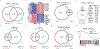









References
-
- Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES & Golub TR A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors. Nat. Genet. 33, 49–54 (2003). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

