Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy Integrated Non-intubated Uniportal VATS in Localization and Resection of Pulmonary Nodules
- PMID: 35449552
- PMCID: PMC9018105
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.872496
Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy Integrated Non-intubated Uniportal VATS in Localization and Resection of Pulmonary Nodules
Abstract
Background: With the development of computed tomography, the detection rate of pulmonary nodules is increasing. Accurate localization, minimally invasive resection, and rapid recovery are the most concentrated issues in modern thoracic surgery. However, some traditional procedures, including CT-guided localization and general intubated anesthesia, might prolong the operation and postoperative recovery. The integrated operating room provides a practical approach to achieve precise pulmonary nodule localization with real-time images using electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB). Meanwhile, the minimally invasive video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) under non-intubated anesthesia is also applied in the same place, enhancing operative efficiency and recovery after surgery.
Method: The patients with pulmonary nodules resection who underwent nodules localization and uniportal VATS under non-intubated anesthesia in the integrated operating room between September 2018 and December 2021 were identified and collected. They all received ENB localization before uniportal VATS under non-intubated anesthesia, provided by the same group of anesthesiologists and surgeons. Perioperative data of patients were analyzed and evaluated to demonstrate the feasibility and efficiency of the procedure.
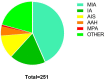
Result: A total of 243 patients with 251 pulmonary nodules underwent ICG staining localization by ENB. The mean calibration time and navigation time were 0.91 ± 0.43 min and 10.56 ± 7.24 min, respectively. Overall, successful navigation occurred in 248 (98.80%) nodules. All patients received thoracoscopic surgery after localization, including wedge resection (231, 92.03%), segmentectomy (13, 5.18%), and lobectomy (7, 2.79%). All nodules were completely resected without serious complications. The mean postoperative hospital was 1.80 ± 0.83 days.
Conclusion: ENB localization and nodules resection under non-intubated uniportal VATS in the integrated operating room provides a feasible and efficient approach to the pulmonary nodules patients, favoring the treatment precision and enhanced recovery.
Keywords: electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy; integrated operating room; non-intubated anesthesia; pulmonary nodule; video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery.
Copyright © 2022 Wang, Jiang, He, Lin, Wang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

