The Prevalence of Demodex Blepharitis in US Eye Care Clinic Patients as Determined by Collarettes: A Pathognomonic Sign
- PMID: 35449733
- PMCID: PMC9017705
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S354692
The Prevalence of Demodex Blepharitis in US Eye Care Clinic Patients as Determined by Collarettes: A Pathognomonic Sign
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the prevalence of Demodex blepharitis by its pathognomonic sign, collarettes, in patients presenting for any reason to eye care clinics in the United States.
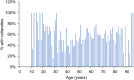
Patients and methods: In this retrospective study by 7 investigators at 6 eye care clinics, case records of consecutive patients who underwent a slit-lamp examination, regardless of chief complaint, were reviewed for Demodex blepharitis, as identified by the presence of collarettes. Patient characteristics, including age, gender, race, relevant ocular and systemic diagnoses, ocular medications, lid hygiene practices and contact lens wear, were also recorded.
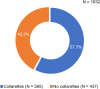
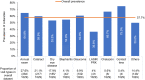
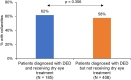
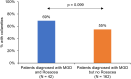
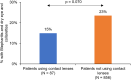
Results: Of 1032 patients (mean age: 60.2 ± 17.8 years), 57.7% had Demodex blepharitis. While the prevalence of Demodex blepharitis in patients with dry eye disease (DED) (58.9%) and cataract (55.7%) was similar to the overall prevalence of Demodex blepharitis, it was higher in patients with blepharitis (69.1%) and glaucoma (64.8%). Among patients with collarettes, 44.0% had never been diagnosed with blepharitis. Among those on anti-inflammatory DED treatment, 60.0% had Demodex blepharitis. Demodex blepharitis prevalence was significantly higher among those using topical tea tree oil versus those who were not (74.5% versus 56.7% p = 0.014); prevalence was comparable among those using/not using lid wipes (56.9% versus 55.5%).
Conclusion: Demodex blepharitis, based on the pathognomonic finding of collarettes, is common and likely underdiagnosed among patients seeking eye care. These collarettes are still found in patients using over-the-counter treatments for blepharitis. The present study highlights the importance of screening patients for collarettes and Demodex blepharitis as part of every slit-lamp examination.
Keywords: Demodex infestation; Demodex mites; collarettes; cylindrical dandruff; lid margin disease; prevalence of Demodex blepharitis.
© 2022 Trattler et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr William Trattler reports grants from Tarsus, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Tarsus, personal fees from Allergan, personal fees from Sun Pharma, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Johnson & Johnson, outside the submitted work; Dr Paul Karpecki reports personal fees from Tarsus Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Oasis Medical, personal fees from BioTissue, personal fees from OcuSoft, personal fees from Danelli Ocular Creations, personal fees from Alcon, personal fees from J&J, outside the submitted work; Dr Yuna Rapoport has nothing to disclose. Dr Ehsan Sadri reports being a consultant for Visionary Eye Institute, outside the submitted work; and Speaker Research Grant. Dr Scott Schachter reports working for Allergan. Dr Walter Whitley reports personal fees from Tarsus Pharmaceuticals, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Tissue Tech, personal fees from Alcon, outside the submitted work. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Amescua G, Akpek EK, Farid M, et al. Blepharitis Preferred Practice Pattern(R). Ophthalmology. 2019;126(1):56–93. - PubMed
-
- Dias MR, Guaresch BLV, Borges CR, Biazim DF, Casagrande D, Luz RA. Blefarite: epidemiologia, etiologia, apresentações clínicas, tratamento e evolução de nossos pacientes. Rev Bras Oftalmol. 2019;78(5):300–303.
-
- Wolffsohn JS, Arita R, Chalmers R, et al. TFOS DEWS II Diagnostic Methodology report. Ocul Surf. 2017;15(3):539–574. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

